A randomised controlled trial (NoMAD trial) showed micronutrients led to faster recovery from depression and anxiety compared with placebo. The RCT was followed by a 10 week open-label component and then a one year naturalistic review.
This 1-year follow-up of NoMAD explored the association between dominant treatment at 1-year follow-up with psychiatric outcomes.
Ninety-four (63 %) of the original 150 NoMAD participants completed 1-year follow-up. Primary outcomes included Generalised Anxiety Disorder-7 questionnaire (GAD-7), Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9), and Modified-Clinical Global Impression-Improvements (MCGI-I). Outcomes were explored based on dominant therapy at 1-year follow-up: Micronutrients (n = 20), Psychiatric Medications (n = 9), and No Treatment (n = 56). Nine participants could not be grouped due to mixed treatments at follow-up.
Regardless of dominant therapy, participants were functioning significantly better at 1-year compared to baseline. There was little change from end of 10 weeks of open-label micronutrient treatment, with the exception of depression scores, which were significantly lower (d = 0.4; p<.001). Most participants had either no or mild depression (78 %) and anxiety (85 %) scores at 1-year follow-up. Those who stayed on micronutrients were those who experienced better response at end of open-label compared with those who stopped or switched to medications. They also showed a greater reduction in health anxiety from end of open-label to 1-year follow-up compared with others. The main reason cited for stopping micronutrients was the cost. Limitations include a third of original sample lost to follow-up and uneven group sizes limit generalisability of results.
Participants, regardless of long-term supplementation, were functioning well at one year.

Coët A, Blampied FM, Rucklidge JJ. 1-year naturalistic follow-up of a Randomised Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial (“NoMAD”) Exploring the Effectiveness of Micronutrients in Improving Symptoms of Anxiety and Depression. Journal of Affective Disorders Reports. Volume 20, April 2025.
Micronutrients have demonstrated promise in managing inattention and emotional dysregulation in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). One plausible pathway by which micronutrients improve symptoms is the gut microbiome. This study examines changes in fecal microbial composition and diversity after micronutrient supplementation in children with ADHD (N = 44) and highlights potential mechanisms responsible for the behavioral improvement, as determined by blinded clinician-rated global improvement response to micronutrients. Participants represent a sub-group of the Micronutrients for ADHD in Youth (MADDY) study, a double blind randomized controlled trial in which participants received micronutrients or placebo for 8 weeks, followed by an 8-week open extension. Stool samples collected at baseline, week 8, and week 16 were analyzed using 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing targeting the V4 hypervariable region. Pairwise compositional analyses investigated changes in fecal microbial composition between micronutrients versus placebo and responders versus non-responders. A significant change in microbial evenness, as measured by alpha diversity, and beta-diversity, as measured by Bray-Curtis, was observed following micronutrients supplementation. The phylum Actinobacteriota decreased in the micronutrients group compared to placebo. Two butyrate-producing bacterial families: Rikenellaceae and Oscillospiraceae, exhibited a significant increase in change following micronutrients between responders versus non-responders. These findings suggest that micronutrients modulated the composition of the fecal microbiota and identified specific bacterial changes associated with micronutrient responders.

Ast HK, Hammer M, Zhang S, Bruton A, Hatsu IE, Leung B, McClure R, Srikanth P, Farris Y, Norby-Adams L, Robinette LM, Arnold LE, Swann JR, Zhu J, Karstens L, Johnstone JM. Gut microbiome changes with micronutrient supplementation in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: the MADDY study. Gut Microbes. 2025 Dec;17(1):2463570. Epub 2025 Feb 18.
Identifying and understanding the genetic contributors to mental health conditions remains a challenge. This is partially due to the complex, polygenic nature of these conditions and the range of underlying genetic variants, including copy number variants (CNV), that contribute to risk. Here we report an individual with severe ADHD who displayed an unusual blood methylome profile, and a strongly positive response during a treatment trial of micronutrients for this condition. The unusual methylome profile prompted a search for structural variants in the genome of this individual, leading to the discovery of two large, rare CNVs, which may help to account for the clinical and epigenetic aspects observed in this case. These CNVs impacted several genes, including RNF4 and EHMT1, both of which encode enzymes involved in DNA methylation, and CACNA1B, which is implicated in neuropsychiatric phenotypes. These CNVs are classified as variants of unknown significance and are likely benign in the clinical setting. Although there is no strong clinical evidence to suggest reclassification of these CNVs, gene regions adjacent to the CNV have been implicated in neuropsychiatric conditions. It seems reasonable to suggest that these rare CNVs may drive the observed perturbation in their methylome profile, and may partially contribute to their ADHD phenotype.

A.J Stevens, M.A Kennedy, K Doudney, MJ.A Kidd, J.J Rucklidge. Potential link between copy number variation and abnormal genome wide DNA methylation profile in an individual with severe ADHD and a strong response to micronutrient treatment. Psychiatry Research Case Reports. 2025.
Aims: Daily broad-spectrum micronutrients are being used by the general public and formulations are receiving research interest in mental health settings. Despite concerns about combining medicines and broad-spectrum micronutrients in mental health care, there have not been any formal evaluations of potential interactions. Our objective was to evaluate a broad-spectrum micronutrient formula as a potential precipitant of pharmacokinetic drug-drug interactions through inhibition or induction of cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes.
Methods: This was a single-centre pharmacokinetic study. Twelve healthy participants received broad-spectrum micronutrients for 14 days (Days 1-14). Participants were administered a 'cocktail' of selective CYP probes midazolam 2 mg (CYP3A), dextromethorphan 30 mg (CYP2D6), losartan 25 mg (CYP2C9), omeprazole 20 mg (CYP2CI9) and caffeine 100 mg (CYP1A2) on Day 0 and Day 14, before taking and while taking broad-spectrum micronutrients. Plasma drug concentrations were measured at baseline and for 8 h following cocktail administration. AUC, Cmax and Tmax were compared before and after broad spectrum micronutrient administration using paired t-tests.
Results: Pre- and post-micronutrient geometric means (SD) for AUC0-8h (μg*h/L) were: midazolam 25 (13) and 26 (14), P = 0.60; dextromethorphan 25 (99) and 19 (110), P = 0.46; losartan 219 (105) and 205 (76), P = 0.20; omeprazole 474 (394) and 402 (342), P = 016; and caffeine 13 800 (5400) and 12 800 (3500), P = 0.79. There were no statistically significant changes in geometric means of probe Cmax, or Tmax for any of the study drugs.
Conclusions: Broad-spectrum micronutrients are unlikely to be a major precipitant of pharmacokinetic drug-drug interactions.

Investigation of a broad-spectrum micronutrient formulation as a possible precipitant of pharmacokinetic micronutrient–drug interactions
Kew BM, Doogue MP, McNeill R, Zhang M, Rucklidge JJ, Frampton CM, Mulder RT, Beaglehole B. Investigation of a broad-spectrum micronutrient formulation as a possible precipitant of pharmacokinetic micronutrient-drug interactions. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2025 Feb 24.
Purpose/background: One-fifth of women experience antenatal depression. Untreated antenatal depression is associated with increased risk of adverse birth outcomes. This study investigated the effect of broad-spectrum micronutrients (BSM; vitamins and minerals), used to treat antenatal depression (NUTRIMUM trial), on birth outcomes.
Methods/procedures: Birth outcomes of 129 mother-infant pairs were obtained from hospital medical records or personal health records for home births. Pairs from NUTRIMUM exposed to ≥8 weeks of BSM antenatally (MN; n = 55) were compared to pairs exposed to antidepressants antenatally (MED; n = 20) and a reference group (REF; n = 54) of pairs not exposed to trial BSM or antidepressants.
Findings/results: Groups were comparable on demographic variables. At study entry, MN and MED had depression scores in the moderate range, statistically higher than REF (nonclinical range). MN and REF did not differ significantly for gestational age, preterm births, infant size, or infant resuscitation. There were significantly lower rates of postpartum hemorrhage in MN relative to REF (7.7% vs 30%; RR = 0.26, 95% CI [0.08-0.84]). Gestational age at birth was higher for MN (39.5 weeks) than MED (38.5 weeks; d = 0.67, 95% CI [0.15-1.20], P = 0.03) as well as infant birth length (52.2 vs 50.0 cm; d = 0.77, 95% CI [0.21-1.33], P = 0.02), and rates of infant resuscitation were lower (14.5% vs 45%; RR = 0.33, 95% CI [0.15-0.73]). Days of BSM exposure was positively associated with birth weight (r = 0.32, P = 0.008) and length (r = 0.25, P = 0.04).
Implications/conclusions: Micronutrients used to alleviate antenatal depression may mitigate negative effects of depression on birth outcomes and showed more favorable birth outcomes compared with antidepressants.

Broad-Spectrum Micronutrients or Antidepressants for Antenatal Depression: Effect on Maternal and Infant Birth Outcomes in an Observational Secondary Analysis of NUTRIMUM
Heaton JL, Campbell SA, Bradley HA, Mulder RT, Dixon L, Henderson J, Rucklidge JJ. Broad-Spectrum Micronutrients or Antidepressants for Antenatal Depression: Effect on Maternal and Infant Birth Outcomes in an Observational Secondary Analysis of NUTRIMUM. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2024 Dec 2.
Background
Broad-spectrum micronutrients (minerals and vitamins) have shown benefit for treatment of depressive symptoms.
Aims
To determine whether additional micronutrients reduce symptoms of antenatal depression.
Method
Eighty-eight medication-free pregnant women at 12–24 weeks gestation, who scored ≥13 on the Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale (EPDS), were randomised 1:1 to micronutrients or active placebo (containing iodine and riboflavin), for 12 weeks. Micronutrient doses were generally between recommended dietary allowance and tolerable upper level. Primary outcomes (EPDS and Clinical Global Impression – Improvement Scale (CGI-I)) were analysed with constrained longitudinal data analysis.
Results
Seventeen (19%) women dropped out, with no group differences, and four (4.5%) gave birth before trial completion. Both groups improved on the EPDS, with no group differences (P = 0.1018); 77.3% taking micronutrients and 72.7% taking placebos were considered recovered. However, the micronutrient group demonstrated significantly greater improvement, based on CGI-I clinician ratings, over time (P = 0.0196). The micronutrient group had significantly greater improvement on sleep and global assessment of functioning, and were more likely to identify themselves as ‘much’ to ‘very much’ improved (68.8%) compared with placebo (38.5%) (odds ratio 3.52, P = 0.011; number needed to treat: 3). There were no significant group differences on treatment-emergent adverse events, including suicidal ideation. Homocysteine decreased significantly more in the micronutrient group. Presence of personality difficulties, history of psychiatric medication use and higher social support tended to increase micronutrient response compared with placebo.
Conclusions
This study highlights the benefits of active monitoring on antenatal depression, with added efficacy for overall functioning when taking micronutrients, with no evidence of harm. Trial replication with larger samples and clinically diagnosed depression are needed.

Efficacy and safety of a mineral and vitamin treatment on symptoms of antenatal depression: 12-week fully blinded randomised placebo-controlled trial (NUTRIMUM)
Bradley HA, Moltchanova E, Mulder RT, Dixon L, Henderson J, Rucklidge JJ. Efficacy and safety of a mineral and vitamin treatment on symptoms of antenatal depression: 12-week fully blinded randomised placebo-controlled trial (NUTRIMUM). BJPsych Open. 2024;10(4):e119.
Objective: With dual focus on structured, objective quantification of parent observations of child's behavior and identifying behaviors most amenable to change, this report examines Parent Target Problems (PTP) as a secondary outcome in a randomized clinical trial (RCT) of children with attention-deficit/ hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in which one primary outcome, Clinical Global Impression-Improvement, showed a significant advantage of multinutrients over placebo and the other, Likert-type parent ratings, showed significant improvement in both groups, without significant difference between them.
Method: In a multisite 8-week RCT of broad-spectrum micronutrients ("multinutrients"), parents of children ages 6-12 (N = 126, 73% male, 88% white) with ADHD and emotional dysregulation nominated their child's most concerning problem(s) at baseline and quantified them by frequency, duration, impairment, and consequences. At subsequent visits, parents re-quantified the problem(s). Blinded child psychiatrists independently reviewed the PTPs and rated change at two timepoints compared to baseline. PTPs were grouped into 9 categories. Mean ratings were compared between active and placebo groups and explored by category.
Results: By week 8, a significant separation favored multinutrients: 38% of the multinutrient group were "definitely improved" or better, compared to 25% of the placebo group, and ratings of "no change" or "worse" occurred in 35% with placebo versus 23% with multinutrients (p = 0.04). Inattention (72.2%) and emotional dysregulation (69.1%) were the most frequently reported PTP categories. Inattention and internalizing symptoms improved more with multinutrients than placebo (p = 0.01, d = 0.55; p = 0.03, d = 0.80, respectively). The multinutrient advantage was not significant for 7 other symptoms, including hyperactivity/impulsivity, aggression, autistic symptoms, or emotional dysregulation/irritable oppositionality.
Conclusions: This secondary analysis found that the multinutrients, compared to placebo, were associated with improvements in parental concerns overall, and in two domains specifically: inattention and internalizing symptoms (anxiety/depression), but not in seven domains: hyperactivity/impulsivity, aggression, autistic symptoms or physiological symptoms, peer relationships or emotional dysregulation/irritable oppositionality.

Problems most concerning to parents of children with ADHD and emotional dysregulation in a randomized controlled trial of multinutrients: MADDY secondary analysis
Tost G, Srikanth P, Bruton A, Hatsu IE, Leung BM, Ast HK, Eiterman LP, Robinette LM, Williams C, Gracious B, Eugene Arnold L, Johnstone JM. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2024 May 31.
Objectives: The 8-week Micronutrients for ADHD in Youth (MADDY) randomized controlled trial (N = 126, age 6-12) of broad-spectrum multinutrients for ADHD with emotional dysregulation found 3 times as many responders with multinutrients (54%) compared to placebo (18%) by Clinical Global Impression-Improvement (CGI-I). Our primary aim for this analysis tests the hypothesis that those with poor overall diet quality at baseline benefit more. The second aim is to explore whether specific components of diet quality moderate treatment response.
Methods: 124 children (69 multinutrients, 55 placebo) had diet quality assessed using the Healthy Eating Index-2015 (HEI-2015). For each potential moderator, the outcome CGI-I at week 8 (RCT-end), was modeled two ways: (1) as a dichotomous variable: responder/non-responder, with responders defined by a rating of 1 or 2 'very much' or 'much improved,' all else equals non-responder using logistic regression, and (2) as a dimensional improvement outcome from 1 = very much improved to 7 = very much worse, using linear regression.
Results: HEI-2015 total score did not moderate treatment response [odds ratio = 1.00 (95% CI: 0.90,1.10), p = 0.984] or improvement [β = -0.01 (95% CI: -0.06,0.04), p = 0.648]. However, total vegetable intake moderated level of improvement in exploratory analysis [β = -0.48 (95% CI: -0.82, -0.13), p = 0.007]: those with higher baseline vegetable intake showed greater benefit from multinutrients compared to placebo.
Conclusions: Multinutrients may benefit children with ADHD and irritability regardless of overall diet quality. The finding that higher baseline vegetable intake may improve response to multinutrients deserves further exploration, including dietary effect on gut microbiota and absorption of multinutrients and parental factors.

Treatment response to supplemental nutrients for ADHD is independent of diet quality: the MADDY Study RCT
Robinette LM, Hatsu IE, Johnstone JM, Bruton AM, Leung BMY, Arnold LE. Treatment response to supplemental nutrients for ADHD is independent of diet quality: the MADDY Study RCT. Nutr Neurosci. 2024 Apr;27(4):319-328.
Background: The Micronutrients for Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder in Youth (MADDY) study evaluated the efficacy and safety of a multinutrient formula for children with ADHD and emotional dysregulation. The post-RCT open-label extension (OLE) compared the effect of treatment duration (8 weeks vs 16 weeks) on ADHD symptoms, height velocity, and adverse events (AEs).
Methods: Children aged 6-12 years randomized to multinutrients vs. placebo for 8 weeks (RCT), received an 8-week OLE for a total of 16 weeks. Assessments included the Clinical Global Impression-Improvement (CGI-I), Child and Adolescent Symptom Inventory-5 (CASI-5), Pediatric Adverse Events Rating Scale (PAERS), and anthropometric measures (height and weight).
Results: Of the 126 in the RCT, 103 (81%) continued in the OLE. For those initially assigned to placebo, CGI-I responders increased from 23% in the RCT to 64% in the OLE; those who took multinutrients for 16 weeks increased from 53% (RCT) to 66% responders (OLE). Both groups improved on the CASI-5 composite score and subscales from week 8 to week 16 (all p-values < 0.01). The group taking 16 weeks of multinutrients had marginally greater height growth (2.3 cm) than those with 8 weeks (1.8 cm) (p = 0.07). No difference in AEs between groups was found.
Conclusion: The response rate to multinutrients by blinded clinician ratings at 8 weeks was maintained to 16 weeks; the response rate in the group initially assigned to placebo improved significantly with 8 weeks of multinutrients and almost caught up with 16 weeks. Longer time on multinutrients did not result in greater AEs, confirming an acceptable safety profile.

Micronutrients for ADHD in youth (MADDY) study: comparison of results from RCT and open label extension.
Leung BMY, Srikanth P, Robinette L, Bruton AM, Tost G, Hatsu I, Arnold LE, Johnstone JM. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2024 May;33(5):1355-1367.
Antenatal depression and maternal nutrition can influence infant temperament. Although broad-spectrum-micronutrients (BSM: vitamins and minerals) given above Recommended Dietary Allowances during pregnancy can mitigate symptoms of antenatal depression, their associated effects on infant temperament are unknown. One hundred and fourteen New Zealand mother-infant dyads (45 infants exposed to BSM during pregnancy (range of exposure during pregnancy: 12-182 days) to treat antenatal depressive symptoms (measured by Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale) and 69 non-exposed infants) were followed antenatally and for 12 months postpartum to determine the influence of in utero BSM exposure on infant temperament. The Infant Behavior Questionnaire-Revised: Very Short-Form assessed temperament at 4 (T1), 6 (T2) and 12 (T3) months postpartum via online questionnaire. Latent growth curve modeling showed BSM exposure, antenatal depression and infant sex did not statistically significantly predict initial levels or longitudinal changes in orienting/regulatory capacity (ORC), positive affectivity/surgency (PAS) or negative affectivity (NEG). Higher gestational age was positively associated with initial PAS, and smaller increases between T1 and T3. Breastfeeding occurrence was positively associated with initial NEG. Although not significant, BSM exposure exerted small, positive effects on initial NEG (β = -0.116) and longitudinal changes in ORC (β = 0.266) and NEG (β = -0.235). While BSM exposure did not significantly predict infant temperament, it may mitigate risks associated with antenatal depression. BSM-exposed infants displayed temperamental characteristics on par with typical pregnancies, supporting the safety of BSM treatment for antenatal depression.

Exploring the impact of antenatal micronutrients used as a treatment for maternal depression on infant temperament in the first year of life
Campbell SA, Dys SP, Henderson JMT, Bradley HA, Rucklidge JJ. Front Nutr. 2024 Apr 22;11:1307701.
The association of household food insecurity with symptoms of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and emotional dysregulation in children was examined in this study. We utilized baseline data from 134 children aged 6-12 years who were enrolled in a clinical trial investigating multinutrient supplementation as a treatment for ADHD and emotional dysregulation. Household food security status was assessed using the 18-item US Household Food Security Survey Module. The symptoms of ADHD and emotional dysregulation disorders (oppositional defiant disorder (ODD) and disruptive mood dysregulation disorder (DMDD)) were assessed using the Child and Adolescent Symptom Inventory-5 and other comorbid emotional dysregulation symptoms were assessed using the Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire (SDQ). Multiple linear regression determined associations between household food security status and symptoms of ADHD, ODD and DMDD, emotional symptoms and conduct problems. Household food insecurity was associated with more severe emotional symptoms (β = 2.30; 95% CI = 0.87-3.73; p = 0.002), conduct problems (β = 1.15; 95% CI = 0.01-2.30; p = 0.049) and total difficulties scores (β = 4.59; 95% CI = 1.82-7.37; p = 0.001) after adjusting for covariates (child's sex, parent marital status, household income, parental anxiety and other parental psychopathology). In unadjusted analyses, household food insecurity was also associated with increased ODD (β = 0.58; 95% CI = 0.21-0.95; p = 0.003) and DMDD symptoms (β = 0.69; 95% CI = 0.20-1.19; p = 0.006), but these associations attenuated to non-significance after adjusting for all covariates. Household food insecurity was associated with more severe emotional dysregulation symptoms. Discussing and addressing food insecurity may be appropriate initial steps for youths with ADHD and emotional dysregulation.

Household Food Insecurity Is Associated with Symptoms of Emotional Dysregulation in Children with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: The MADDY Study.
Hatsu IE, Eiterman L, Stern M, Lu S, Johnstone JM, Leung BMY, Srikanth P, Robinette L, Tost G, Odei JB, Gracious BL, Arnold LE. Household Food Insecurity Is Associated with Symptoms of Emotional Dysregulation in Children with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: The MADDY Study. Nutrients. 2022 Mar 20;14(6):1306.
Background: Antenatal depression is a risk factor for poor infant outcomes. Broad-spectrum-micronutrients (vitamins and minerals) have shown efficacy in treating psychiatric symptoms in non-pregnant populations and are associated with reduced incidence of adverse birth outcomes, and improvements in neonatal development. We investigated the effects of treatment of antenatal depression with micronutrients above the Recommended Dietary Allowance on infant development compared to treatment with antidepressant medications and controls.
Method: One-hundred-and-three infants were assessed using the Brazelton Neonatal Behavioral Assessment Scale (NBAS) within 28 days of birth: 37 exposed to micronutrients in-utero (50-182 days exposure), 18 to antidepressants in-utero (exposure for full gestation), and 48 controls whose mothers received neither treatment nor experienced depressive symptoms.
Results: Controlling for gestational age and parity, there were significant group differences on habituation, orientation, motor, state regulation, autonomic stability and reflexes (p < .05). Micronutrient-exposed performed better than antidepressant-exposed and controls on habituation, motor and autonomic stability (p < .05), effect sizes ranged 1.0-1.7 and 0.5-1.0, respectively. Antidepressant-exposed performed significantly worse on orientation and reflexes compared to micronutrient-exposed and controls. Micronutrient-exposed had significantly better state regulation compared to antidepressant-exposed. There was an association between micronutrient exposure length and better habituation (r = 0.41, p = .028). Micronutrient exposure was generally identified as a stronger predictor of neonatal performance over maternal depression, social adversity, gestational age and infant sex.
Conclusion: In-utero micronutrient exposure appears to mitigate risks of depression on infant outcomes showing positive effects on infant behavior, on par with or better than typical pregnancies and superior to antidepressants. Limitations include differential exposure to micronutrients/antidepressants and lack of group blinding.

Effect of antenatal micronutrient or antidepressant exposure on Brazelton neonatal behavioral assessment scale (NBAS) performance within one-month of birth
Campbell SA, Bradley HA, Mulder RT, Henderson JMT, Dixon L, Haslett LC, Rucklidge JJ. Effect of antenatal micronutrient or antidepressant exposure on Brazelton neonatal behavioral assessment scale (NBAS) performance within one-month of birth. Early Hum Dev. 2024 Mar;190:105948.
Background: Anxiety and depression are increasingly burdening society. We investigated whether micronutrients (vitamins and minerals), improve anxiety and depression symptoms in an adult community setting.
Methods: Participants (n = 150) describing functionally-impairing symptoms of anxiety/depression randomly received micronutrients or placebo for 10 weeks. Primary outcome measures were Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9), Generalised Anxiety Disorder Scale-7 (GAD-7), and Clinical Global Impression-Improvement scale (CGII). They were monitored online with regular phone contact with a clinical psychologist.
Results: Linear mixed-effects modelling showed significant improvements in both groups, with the micronutrient group improving significantly more quickly on both the PHQ-9 (t = -2.17, p = 0.03) and the GAD-7 (t = -2.23, p = 0.03). Subsequent models with covariates showed that participant characteristics moderated time-by-group interactions; micronutrients provided fastest improvement relative to placebo for younger participants, those from lower socioeconomic groups and those who had previously tried psychiatric medication. On the CGII, there were no group differences at end-point ((F1,148) = 1.36, p = 0.25, d = 0.19, 95 % CI [-0.13 to 0.51]), with 49 % of the micronutrient and 44 % of the placebo groups being identified responders. Participants on micronutrients had significantly increased bowel motions compared with placebo. There was no increased suicidal ideation, no serious adverse events and the blind was adequately maintained. Drop out was low at 8.7 %.
Limitations: The improvement under placebo and lack of formal diagnoses limit generalizability.
Conclusions: Despite limited clinician contact, all participants improved significantly, though improvements were faster with micronutrients. Participants in some subgroups demonstrated a lower response to placebo, identifying where micronutrients may offer greatest potential as an intervention.

Efficacy and safety of a vitamin-mineral intervention for symptoms of anxiety and depression in adults: A randomised placebo-controlled trial “NoMAD”
Blampied FM, Tylianakis JM, Bell C, Gilbert C, Rucklidge JJ. Efficacy and safety of a vitamin-mineral intervention for symptoms of anxiety and depression in adults: A randomised placebo-controlled trial "NoMAD". J Affect Disord. 2023 May 31:S0165-0327(23)00718-8.
Conclusions
Multinutrients combining 4 or more ingredients, mindfulness, and polyunsaturated fatty acids showed replicated, consistent moderate effects and can be encouraged as secondary treatments in combination with primary treatments or if a primary treatment is not a fit for the participant and their family.
Summary
Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) affects approximately 5% of children and adolescents globally and
is associated with negative life outcomes and socioeconomic costs. First-generation ADHD treatments were
predominantly pharmacological; however, increased understanding of biological, psychological, and environmental
factors contributing to ADHD has expanded non-pharmacological treatment possibilities. This Review provides
an updated evaluation of the efficacy and safety of non-pharmacological treatments for paediatric ADHD,
discussing the quality and level of evidence for nine intervention categories. Unlike medication, no
non-pharmacological treatments showed a consistent strong effect on ADHD symptoms. When considering broad
outcomes (eg, impairment, caregiver stress, and behavioural improvement), multicomponent (cognitive)
behaviour therapy joined medication as a primary ADHD treatment. With respect to secondary treatments,
polyunsaturated fatty acids showed a consistent modest effect on ADHD symptoms when taken for at least
3 months. Additionally, mindfulness and multinutrient supplementation with four or more ingredients showed
modest efficacy on non-symptom outcomes. All other non-pharmacological treatments were safe; clinicians might
tolerate their use but should educate families of childrenand adolescents with ADHD on the disadvantages,
including costs, burden to the service user, absence of proven efficacy relative to other treatments, and delay of
proven treatment.

Non-pharmacological interventions for attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents
Sibley MH, Bruton AM, Zhao X, Johnstone JM, Mitchell J, Hatsu I, Arnold LE, Basu HH, Levy L, Vyas P, Macphee F, Gonzalez ES, Kelley M, Jusko ML, Bolden CR, Zulauf-McCurdy C, Manzano M, Torres G. Non-pharmacological interventions for attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2023 Mar 9:S2352-4642(22)00381-9.
Elevated inflammation has been associated with adverse mood states, such as depression and anxiety, and antioxidant nutrients, such as vitamin C, have been associated with decreased inflammation and improved mood. In the current study comprising a cohort of pregnant women with depression and anxiety, we hypothesised that elevated inflammation would be associated with adverse mood states and inversely associated with vitamin C status and that multinutrient supplementation would optimise vitamin concentrations and attenuate inflammation. Sixty-one participants from the NUTRIMUM trial had blood samples collected between 12 and 24 weeks gestation (baseline) and following 12 weeks of daily supplementation with a multinutrient formula containing 600 mg of vitamin C or active placebo. The samples were analysed for inflammatory biomarkers (C-reactive protein (CRP) and cytokines) and vitamin C content and were related to scales of depression and anxiety. Positive correlations were observed between interleukin-6 (IL-6) and all of the mood scales administered (p < 0.05), including the Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale, the Clinical Global Impressions-Severity Scale, the Montgomery and Åsberg Depression Rating Scale, the Depression Anxiety Stress Scale 21, and the Generalized Anxiety Disorder-7 (GAD-7). CRP correlated weakly with GAD-7 (p = 0.05). There was an inverse correlation between CRP and the vitamin C status of the cohort (p = 0.045), although there was no association of the latter with the mood scales (p > 0.05). Supplementation with the multinutrient formula resulted in a significant increase in the vitamin C status of the cohort (p = 0.007) but did not affect the inflammatory biomarker concentrations (p > 0.05). In conclusion, greater systemic inflammation was associated with worse mood states; however, 12-week multinutrient supplementation did not alter inflammatory biomarker concentrations. Nevertheless, the vitamin C status of the cohort was improved with supplementation, which may aid pregnancy and infant outcomes.

Inflammation and Vitamin C in Women with Prenatal Depression and Anxiety: Effect of Multinutrient Supplementation.
Carr AC, Bradley HA, Vlasiuk E, Pierard H, Beddow J, Rucklidge JJ. Inflammation and Vitamin C in Women with Prenatal Depression and Anxiety: Effect of Multinutrient Supplementation. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Apr 17;12(4):941.
The Micronutrients for ADHD in Youth (MADDY) study was an 8-week double-blind RCT of broad spectrum multinutrients (BSMN) for ADHD with emotional dysregulation in children ages 6–12. Primary outcome Clinical Global Impressions-Improvement (CGI-I) showed 3 times as many responders with BSMN (54%) as placebo (18%). Since diet is the primary source of nutrients intake, and diet quality corresponds with nutritional outcomes, this study seeks to determine the role of baseline diet quality as a moderator of treatment response to test the hypothesis that those with poor diet quality should benefit more.
124 children (69 BSMN, 55 placebo) in the intent-to-treat analysis had diet quality assessed by Healthy Eating Index-2015 (HEI-2015) component and total scores from the VioscreenTM FFQ. Primary outcome was odds of treatment response, defined by a rating of 1 or 2 (very much or much improved) on CGI-I at week 8. Sensitivity analysis used CGI-I at week 8 as a dimensional outcome (from 1 = very much improved to 7 = very much worse). Logistic regressions were conducted for the primary analysis and linear regressions for the sensitivity analysis, with HEI scores entered as potential moderators.
Total HEI-2015 score did not moderate treatment response [odds ratio = 1.00 (95% CI: 0.90,1.10), p = 0.994] or improvement [β= −0.01 (95% CI: −0.06,0.04), p = 0.655]. HEI component scores also did not moderate treatment response, though total vegetable intake moderated level of improvement [β= −0.48 (95% CI: −0.82, −0.13), p = 0.007]: those with higher vegetable intake showed greater improvement with BSMN but not with placebo.
BSMN may benefit children with ADHD and irritability regardless of diet quality. The finding that higher baseline vegetable intake possibly predisposes to improvement with BSMN is puzzling and worth further exploration of potential mechanisms such that a higher vegetable intake may promote the absorption or utilization of the multinutrients.

Diet Quality as a Moderator of Response to Multinutrients for ADHD and Emotional Dysregulation: The MADDY RCT.
Robinette L, Hatsu I, Johnstone J, Leung B, Arnold LE. Diet Quality as a Moderator of Response to Multinutrients for ADHD and Emotional Dysregulation: The MADDY RCT. Curr Dev Nutr. 2022 Jun 14;6(Suppl 1):395.
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate whether micronutrients (vitamins/minerals) benefit attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and irritability in a North American pediatric sample.
Method: A three-site 8-week placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial of micronutrients was conducted in unmedicated children ages 6-12 with ADHD and at least one impairing irritability symptom by parent report on the Child and Adolescent Symptom Inventory-5 (CASI-5). A priori-defined primary outcomes were Clinical Global Impression-Improvement (CGI-I) (CGI-I of 1 or 2 = treatment responder) and parent-rated CASI-5 composite score of ADHD, oppositional defiant, disruptive mood dysregulation, and peer conflict symptoms, including impairment scores.
Results: Of 135 randomized (mean age 9.8 years), 126 (93%) comprised the modified intention-to-treat population. Blinding was maintained. For the CGI-I, 54% of the micronutrient and 18% of the placebo group were responders (Risk Ratio=2.97, 97.5% CI: 1.50, 5.90, p<0.001). CASI-5 composite scores improved significantly for both groups (p<0.01) with a mean change of -0.31 (95% CI: -0.39, -0.23) in the micronutrient group and a mean change of -0.28 (95% CI: -0.38, -0.19) in the placebo group. But the between group difference was not significant (mean change = -0.02; 97.5% CI: -0.16, 0.12, ES = 0.07, p=0.70). The micronutrient group grew six millimeters more than the placebo group (p=0.002). No serious adverse events nor clinically significant changes from baseline in blood and urine tests occurred.
Conclusion: Micronutrients showed global benefit over placebo by blinded clinician rating, but not by parent-report CASI-5 composite rating in a population with ADHD and irritability. Micronutrients showed greater height growth. Micronutrients were well tolerated and the majority adhered to the number of capsules prescribed. This RCT replicates safety and efficacy reported for ADHD in two smaller trials of a similar formula containing all vitamins and known essential minerals in amounts between the Recommended Dietary Allowance and Upper Tolerable Intake Level.

Micronutrients for Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder in Youth: A Placebo-Controlled Randomized Clinical Trial
Johnstone JM, Hatsu I, Tost G, Srikanth P, Eiterman LP, Bruton A, Ast HK, Robinette LM, Stern MM, Millington EG, Gracious B, Hughes AJ, Leung BM, Arnold LE. Micronutrients for Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder in Youth: A Placebo-Controlled Randomized Clinical Trial. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2021 Jul 21:S0890-8567(21)00473-1.
ABSTRACT
Objective: The Pediatric Adverse Event Rating Scale (PAERS) measured adverse events of children
aged 6–12 years with ADHD and emotional dysregulation in the Micronutrients for ADHD in Youth
(MADDY) study, an eight week multi-site randomized clinical trial of a broad-spectrum multinutrient
treatment. Treatment sensitivity of the PAERS was assessed by calculating the treatment difference in
change of the item scores from baseline to end of the RCT.
Methods: Principal component analysis retained 14 “adverse events” (out of 43 in the PAERS) that
reflected ADHD symptoms and emotional dysregulation and was used to group the variables of interest.
A combined score ranging from 0 to 5 was created based on symptom presence, functional
impairment, and severity. Mean score change was calculated from baseline to week 8 by treatment
(multinutrient vs placebo) with intention-to-treat and per-protocol samples. The study has been registered
on clinicaltrials.gov as Micronutrients for ADHD in Youth (MADDY) Study, trial registration #
NCT03252522 (https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03252522).
Results: The 126 children in the ITT sample had a mean age of 9.8 (SD = 1.7), with majority (73%)
male, and 72% diagnosed with ADHD prior to the study screening. Baseline presence of PAERS symptoms
was similar between treatment groups: the highest proportion was ADHD symptoms, followed
by Irritable symptoms. The micronutrient group showed a greater decrease (improvement) in the
mean anxiety combined score than the placebo group with a between-group difference in change of
- 0.36 (95% CI: - 0.67, - 0.04; p¼.03) with ITT data and - 0.48 (95% CI: - 0.81, - 0.15; p = .005) with
per-protocol (n = 93) data.
Conclusion: The multinutrient supplement did not result in more adverse events than placebo, suggesting
it is a safe intervention. In addition to assessing actual adverse events, the PAERS may be a
useful adjunct outcome measure for ADHD behaviors.

Paediatric adverse event rating scale: a measure of safety or efficacy? Novel analysis from the MADDY study
Brenda M. Y. Leung, Priya Srikanth, Barbara Gracious, Irene E. Hatsu, Gabriella Tost, Valerie Conrad, Jeanette M. Johnstone & L. Eugene Arnold (2022) Paediatric adverse event rating scale: a measure of safety or efficacy? Novel analysis from the MADDY study, Current Medical Research and Opinion, 2022 Sep;38:9, 1595-1602.
The 'Micronutrient Formula' rated by this international taskforce was Daily Essential Nutrients, and was given an 'Evidence Grade' of 'A', due to a statistically significant meta-analysis (k = 2, n = 173) with statistically significant RCTs in adult and child samples. They gave the following supporting statements for Daily Essential Nutrients:
Meta-analytic level results have shown supportive evidence for efficacy in ADHD as a monotherapy
More replicated evidence required (in both adults and children)
This particular micronutrient formula’s efficacy cannot necessarily be extended to other multi-nutrient formulas
Dosing may need to be supervised (and titrated) via a health profession
Cost and compliance may be an issue due to a recommended dosage of 8–12 capsules per day
Acceptable safety data
Objectives: The therapeutic use of nutrient-based 'nutraceuticals' and plant-based 'phytoceuticals' for the treatment of mental disorders is common; however, despite recent research progress, there have not been any updated global clinical guidelines since 2015. To address this, the World Federation of Societies of Biological Psychiatry (WFSBP) and the Canadian Network for Mood and Anxiety Disorders (CANMAT) convened an international taskforce involving 31 leading academics and clinicians from 15 countries, between 2019 and 2021. These guidelines are aimed at providing a definitive evidence-informed approach to assist clinicians in making decisions around the use of such agents for major psychiatric disorders. We also provide detail on safety and tolerability, and clinical advice regarding prescription (e.g. indications, dosage), in addition to consideration for use in specialised populations.
Methods: The methodology was based on the WFSBP guidelines development process. Evidence was assessed based on the WFSBP grading of evidence (and was modified to focus on Grade A level evidence - meta-analysis or two or more RCTs - due to the breadth of data available across all nutraceuticals and phytoceuticals across major psychiatric disorders). The taskforce assessed both the 'level of evidence' (LoE) (i.e. meta-analyses or RCTs) and the assessment of the direction of the evidence, to determine whether the intervention was 'Recommended' (+++), 'Provisionally Recommended' (++), 'Weakly Recommended' (+), 'Not Currently Recommended' (+/-), or 'Not Recommended' (-) for a particular condition. Due to the number of clinical trials now available in the field, we firstly examined the data from our two meta-reviews of meta-analyses (nutraceuticals conducted in 2019, and phytoceuticals in 2020). We then performed a search of additional relevant RCTs and reported on both these data as the primary drivers supporting our clinical recommendations. Lower levels of evidence, including isolated RCTs, open label studies, case studies, preclinical research, and interventions with only traditional or anecdotal use, were not assessed.
Conclusions: Based on the current data and clinician input, a range of nutraceuticals and phytoceuticals were given either a supportive recommendation or a provisional recommendation across a range of various psychiatric disorders. However several had only a weak endorsement for potential use; for a few it was not possible to reach a clear recommendation direction, largely due to mixed study findings; while some other agents showed no obvious therapeutic benefit and were clearly not recommended for use. It is the intention of these guidelines to inform psychiatric/medical, and health professional practice globally.

Clinician guidelines for the treatment of psychiatric disorders with nutraceuticals and phytoceuticals: The World Federation of Societies of Biological Psychiatry (WFSBP) and Canadian Network for Mood and Anxiety Treatments (CANMAT) Taskforce
Sarris J, Ravindran A, Yatham LN, Marx W, Rucklidge JJ, McIntyre RS, Akhondzadeh S, Benedetti F, Caneo C, Cramer H, Cribb L, de Manincor M, Dean O, Deslandes AC, Freeman MP, Gangadhar B, Harvey BH, Kasper S, Lake J, Lopresti A, Lu L, Metri NJ, Mischoulon D, Ng CH, Nishi D, Rahimi R, Seedat S, Sinclair J, Su KP, Zhang ZJ, Berk M. Clinician guidelines for the treatment of psychiatric disorders with nutraceuticals and phytoceuticals: The World Federation of Societies of Biological Psychiatry (WFSBP) and Canadian Network for Mood and Anxiety Treatments (CANMAT) Taskforce. World J Biol Psychiatry. 2022 Jul;23(6):424-455.
Background: Parents' lived experiences of having a child with ADHD may shape their decision making regarding ADHD treatment options for their child. The aim of this study was to explore parents' experiences of living with a child with ADHD in the family and how their experiences influence their perspectives on treatment preferences and priorities.
Methods: A phenomenological qualitative design was used. Semistructured interviews were conducted with parents of children with ADHD who were enrolled in a multisite randomized controlled trial. Interviews were transcribed verbatim, and transcripts at each site were double coded. Initial codes were derived directly from the text. Qualitative data were analysed with an inductive approach.
Results: Twenty-three parents were interviewed: eight from Alberta, Canada; eight from Portland, Oregon, USA; and seven from Columbus, Ohio, USA. Among the parents, 69% were married, 86% completed college education and 52% reported household income over $80,000. Among the children, the mean age was 9.6 years (SD = 1.8 years), 78% were boys and 48% were never medicated for their ADHD. Two major themes emerged from the analysis. Theme 1 was 'impact of ADHD on families within and outside the home' with the following subthemes: 'reconfiguring the home life', 'trial-and-error of accommodations at school' and 'responding to social pressures to fit in'. Theme 2 was 'enabling appropriate and accessible treatments for families' with the following subthemes: 'finding the "right fit" with professionals and treatments' and 'factors influencing inequitable access to treatments'.
Conclusions: Parents described shared experiences and identified similar barriers, preferences and priorities for ADHD treatments regardless of demographic differences by site. Families desired access to family-centred, multimodal approaches to ADHD treatment. Further research is needed to identify the specific structural changes to healthcare, services and policies that will better support this approach.

Parents' priorities and preferences for treatment of children with ADHD: Qualitative inquiry in the MADDY study
Lu SV, Leung BMY, Bruton AM, Millington E, Alexander E, Camden K, Hatsu I, Johnstone JM, Arnold LE. Parents' priorities and preferences for treatment of children with ADHD: Qualitative inquiry in the MADDY study. Child Care Health Dev. 2022 Sep;48(5):852-861.
Objective: We investigated whether changes in serum nutrient levels mediate clinical response to a micronutrient intervention for ADHD. Method: Data were compiled from two ADHD trials (8-10 weeks), one in adults† (n = 53) and one in children (n = 38). Seven outcomes included change in ADHD symptoms, mood, overall functioning (all clinician-rated) as well as response status. Change in serum/plasma nutrient levels (vitamins B12 and D, folate, ferritin, iron, zinc, and copper) were considered putative mediators. Results: A decrease in ferritin and an increase in copper were weakly associated with greater likelihood of being identified as an ADHD responder; none of the other nutrient biomarkers served as mediators. Conclusion: Further research looking at nutrients more broadly from other tissues are required to confirm these initial observations of the limited value of nutrient levels in deciphering mechanism of action. Monitoring these biomarkers on their own is unlikely helpful in understanding clinical response to a broad-spectrum micronutrient approach.

Do Changes in Blood Nutrient Levels Mediate Treatment Response in Children and Adults With ADHD Consuming a Vitamin-Mineral Supplement?
Rucklidge JJ, Eggleston MJF, Boggis A, Darling K, Gorman B, Frampton CM. J Atten Disord. 2021 Jun;25(8):1107-1119. Epub 2019 Nov 9.
Abstract
This systematic review and meta-analysis focused on randomized controlled trials (RCT) of multinutrients consisting of at least four vitamins and/or minerals as interventions for participants with psychiatric symptoms. A systematic search identified 16 RCTs that fit the inclusion criteria (n = 1719 participants) in six psychiatric categories: depression, post-disaster stress, antisocial behavior, behavioral deficits in dementia, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, and autism. Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development and Evaluations (GRADE) was used to rate the evidence base. Significant clinical benefit was assessed using minimal clinically important differences (MIDs). Due to heterogeneity in participants, multinutrient formulas, outcome measures, and absence of complete data, only the Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) category was eligible for meta-analyses. In ADHD populations, statistically and clinically significant improvements were found in global functioning, Mean Difference (MD) -3.3, p = 0.001, MID -3.26; Standardized Mean Difference (SMD) -0.49 p = 0.001 MD -0.5), clinician ratings of global improvement (MD -0.58, p = 0.001, MID -0.5) and ADHD improvement (MD -0.54, p = 0.002, MID -0.5), and clinician (but not observer) measures of ADHD inattentive symptoms (MD -1.53, p = 0.05, MID -0.5). Narrative synthesis also revealed a pattern of benefit for global measures of improvement, for example: in autism, and in participants with behavioral deficits in dementia. Post-natural disaster anxiety and the number of violent incidents in prison populations also improved. Broad-spectrum formulas (vitamins + minerals) demonstrated more robust effects than formulas with fewer ingredients. This review highlights the need for robust methodology-RCTs that report full data, including means and standard deviations for all outcomes-in order to further elucidate the effects of multinutrients for psychiatric symptoms.
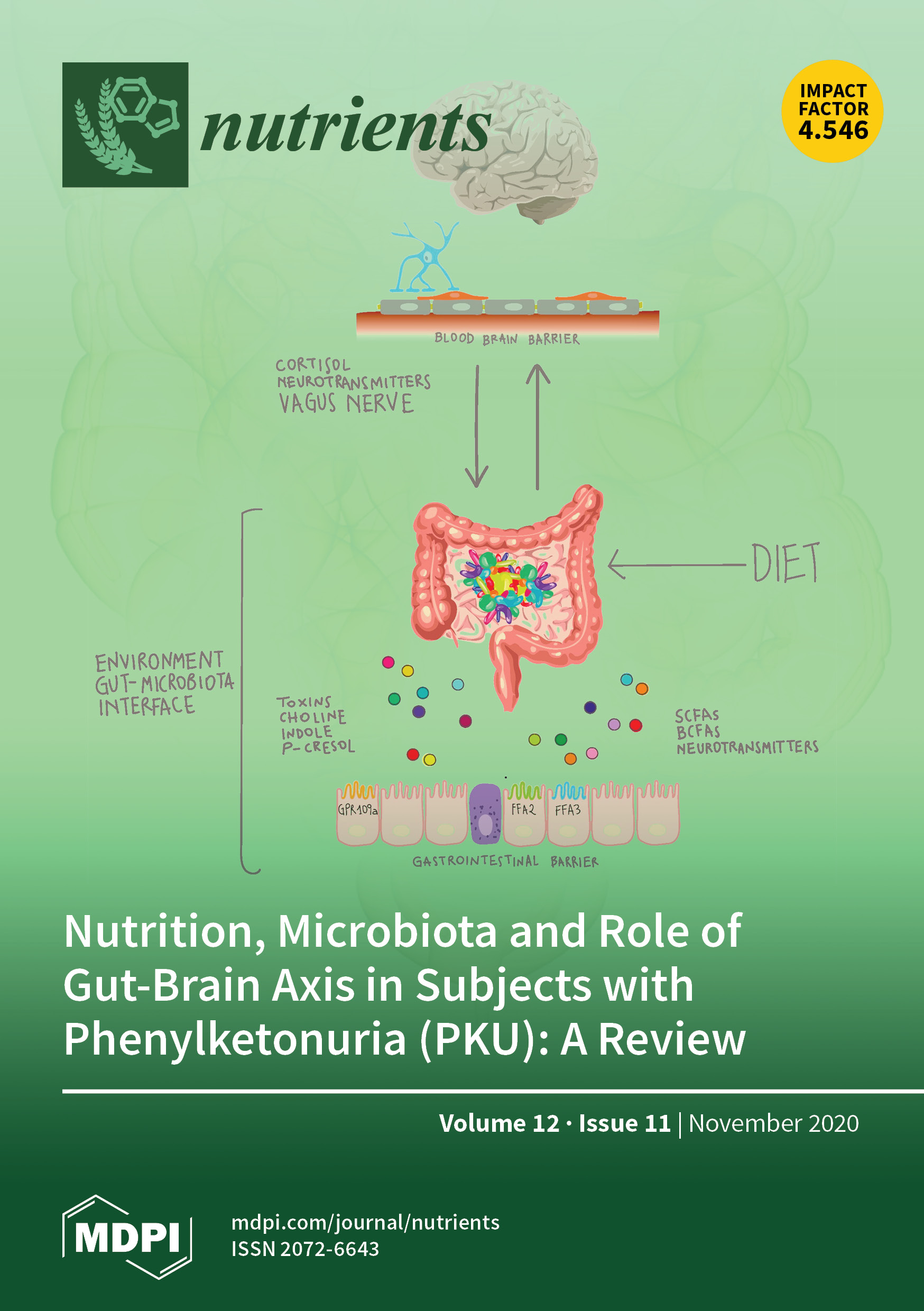
Multinutrients for the Treatment of Psychiatric Symptoms in Clinical Samples: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Jeanette M Johnstone, Andrew Hughes, Joshua Z Goldenberg, Amy R Romijn, Julia J Rucklidge. Nutrients. 2020 Nov 4;12(11):3394.
Abstract
A package of biopsychosocial services for young adults experiencing psychological distress was evaluated and compared to usual outpatient psychiatric care. Young adults (18–25) with moderate-to-severe symptoms of depression and/or anxiety (n = 26) were enrolled in a 13-week intervention consisting of nutritional coaching and multi-vitamin supplements, weekly educational and peer support groups, and a modest financial stipend to engage with physical or expressive activities. A comparison group (n = 13) continued with their usual medication-based outpatient care. Program participants reported significantly improved depression, anxiety, severity of distress, overall quality of life, and empowerment over 4 months, with progress maintained or further improved at 2-month follow-up. No evidence of change on any outcome was observed for comparison group participants. Although long-term impacts on mental health trajectories and reliance on psychotropic medications remain unknown, a holistic self-learning approach is a viable alternative to standard outpatient psychiatric care for young adults.

A Holistic Self‑learning Approach for Young Adult Depression and Anxiety Compared to Medication‑Based Treatment‑As‑Usual
Shannon Hughes, Mary Rondeau, Scott Shannon, Julia Sharp, Grace Ivins, JeongJin Lee, Ian Taylor, Brianna Bendixsen. Community Ment Health J. 2020 Jun 23.
Children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) show significant abnormalities on MR imaging in network communication and connectivity. The prefrontal-striatal-cerebella circuitry, involved in attention is particularly disrupted. Neurometabolites, the biochemical structures that support neurological structural integrity, particularly in the prefrontal cortex and striatum are associated with symptoms. This study aimed to explore changes in neurometabolite levels through treatment with vitamins and minerals (micronutrients), hypothesising that treatment would impact neural circuitry and correspond to a reduction in symptoms. Twenty-seven non-medicated children (M = 10.75 years) with DSM5 diagnosed ADHD were randomised to receive daily micronutrients or placebo for 10 weeks. Main outcome measures included the Clinical Global Impression-Improvement Scale and ADHD-RS-IV Clinician Ratings of ADHD symptoms. Magnetic resonance spectroscopy of the bilateral pre-frontal cortex and bilateral striatum, resting state fMRI and structural images were acquired 1 week pre-treatment, and in the last week of intervention. Results did not show any significant differences in the measured brain metrics and the levels of neurometabolites between treatment and placebo groups after ten weeks of treatment with micronutrients. In the treatment group there was a trend for: decreased choline in the striatum; decreased glutamate in the prefrontal cortex; increased grey matter in the anterior thalamus; increased white matter in the fornix and improved network integrity of the default mode network, dorsal attention network and frontal executive network. The small sample size of the current study limits results, future studies with higher power are warranted to explore any association between micronutrient treatment and neurological changes.

Resting-state networks and neurometabolites in children with ADHD after 10 weeks of treatment with micronutrients: results of a randomised placebo-controlled trial
Borlase N, Melzer TR, Eggleston MJF, Darling KA, Rucklidge JJ. Nutr Neurosci. 2020 Nov;23(11):876-886.
Introduction
Many smokers do not achieve abstinence using current smoking cessation options. This randomized controlled trial (RCT) investigated a novel nutritional supplement to assist with quitting smoking.
Methods
Following a baseline phase where cigarettes per day and nicotine dependence were measured, participants (n = 107) were randomized to placebo (n = 50) or micronutrient conditions (n = 57). A 4-week pre-quit phase permitted titration up to 12 capsules/day. During the quit phase (12 weeks), participants were registered with a public Quitline while consuming micronutrients or placebo. Carbon monoxide levels were measured to confirm smoking cessation.
Results
Forty-five (42%) participants completed the trial. Treatment and placebo groups did not differ on the primary outcome of continuous abstinence at 12 weeks using intention-to-treat analysis; however, 28% of the micronutrient-treated group had quit versus 18% for placebo (odds ratio [OR] = 1.78, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 0.71 to 4.48), with number needed to treat = 10. Comparison of cigarette consumption (cigarettes per day) between micronutrient and placebo groups showed that those taking micronutrients reported reduced consumption throughout the trial, notably at pre-quit weeks 1 and 4, and at quit phase week 4. There were no serious adverse events, blinding was successful, and there were no substantive group differences in side effects or dropout rate.
Conclusion
This is the first RCT investigating the impact of micronutrients on smoking reduction, finding that micronutrients reduced harm through reduction in number of cigarettes smoked relative to placebo. The small sample and high dropout rate limit confidence in the conclusions and generalizability of the study; however, assessed by number needed to treat, micronutrients are comparable to other smoking cessation treatments but with fewer side effects. Future research using larger and longer trials including cost-effectiveness and biomarker measures is encouraged.
Implications
Micronutrients are being increasingly studied for the treatment of psychiatric conditions, but direct application of micronutrients as a treatment for addictions is novel. There is extensive evidence that micronutrients alleviate stress. Given that tobacco smoking is often used to cope with stress, taking micronutrients may moderate the stress of withdrawal and increase the chance of a successful quit attempt. This study is the first known RCT to investigate the use of micronutrients to support smoking cessation. Treatments that are safe, effective, relatively inexpensive, and readily available are needed and micronutrient supplements offer one such possible alternative.

Novel Mineral–Vitamin Treatment for Reduction in Cigarette Smoking: A Fully Blinded Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial
Phillipa K Reihana, Neville M Blampied, Julia J Rucklidge. Nicotine Tob Res. 2019 Oct 26;21(11):1496-1505.
Abstract
It has been widely hypothesized that both diet and the microbiome play a role in the regulation of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) behaviour. However, there has been very limited scientific investigation into the potential biological connection. We performed a 10-week pilot study investigating the effects of a broad spectrum micronutrient administration on faecal microbiome content, using 16S rRNA gene sequencing.
The study consisted of 17 children (seven in the placebo and ten in the treatment group) between the ages of seven and 12 years, who were diagnosed with ADHD. We found that micronutrient treatment did not drive large-scale changes in composition or structure of the microbiome.
However, observed OTUs significantly increased in the treatment group, and showed no mean change in the placebo group. The differential abundance and relative frequency of Actinobacteria significantly decreased post- micronutrient treatment, and this was largely attributed to species from the genus Bifidobacterium. This was compensated by an increase in the relative frequency of species from the genus Collinsella.
Further research is required to establish the role that Bifidobacterium contribute towards neuropsychiatric disorders; however, these findings suggest that micronutrient administration could be used as a safe, therapeutic method to modulate Bifidobacterium abundance, which could have potential implications for modulating and regulating ADHD behaviour.
Our pilot study provides an initial observation into this area of research, and highlights an interesting avenue for further investigation in a larger cohort. Furthermore, these novel results provide a basis for future research on the biological connection between ADHD, diet and the microbiome.
Human gut microbiome changes during a 10 week Randomised Control Trial for micronutrient supplementation in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
Aaron J. Stevens, Rachel V. Purcell, Kathryn A. Darling, Matthew J. F. Eggleston, Martin A. Kennedy & Julia J. Rucklidge. Scientific Reportsvolume 9, Article number: 10128, 2019
Abstract
Objective: This article presents 1-year follow-up of a randomized placebo-controlled trial with open-label extension evaluating the efficacy of a broad-spectrum micronutrient (vitamins and minerals) intervention. The object was to determine if dominant treatment at follow-up was associated with differential psychological outcomes.
Methods: Ninety percent of the original sample of 93 children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) were followed 52 weeks postbaseline. Assessments included measures of ADHD, mood, anxiety, and general function based on parent/clinician report. Outcome was considered based on dominant therapy at 52 weeks (trial micronutrients [n = 19], medications [n = 21], and no treatment [n = 35]). Nine children were not categorized due to inconsistent therapies.
Results: Based on dominant treatment, more of those who stayed on trial micronutrients (84%) were identified as “Much” or “Very Much” improved overall relative to baseline functioning, compared to 50% of those who switched to psychiatric medications and only 21% of those who discontinued treatment [χ2(2) = 19.476, p < 0.001]. Fifteen (79%) of those still taking micronutrients, 8 (42%) of those using medications, and 7 (23%) of those who discontinued treatment were considered remitters based on parent-reported ADHD [χ2(2) = 15.3, p < 0.001]. Those who stayed on micronutrients were more likely to have failed medication treatment in the past. The micronutrient group also displayed better outcomes on measures of parent-rated hyperactivity and anxiety, and clinician-rated general function and mood, with moderate to large between-group effect sizes (micronutrients vs. medication: ES = 0.73–1.01; micronutrients vs. no treatment: ES = 0.54–1.01). Most common reasons for stopping trial micronutrients were cost and number of pills to swallow. No continued side effects were associated with micronutrients.
Conclusions: Children who benefitted from micronutrients in the short term maintained changes at follow-up, without side effects. While both those who continued micronutrients and those who switched to medication showed improved ADHD symptoms, psychiatric medication use was associated with deterioration in mood and anxiety. Inherent selection bias limits generalizability.

Mineral-Vitamin Treatment Associated with Remission in Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder Symptoms and Related Problems: 1-Year Naturalistic Outcomes of a 10-Week Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial
Kathryn A. Darling, Matthew J.F. Eggleston, Hannah Retallick-Brown, and Julia J. Rucklidge. Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychopharmacology 25 Jul 2019 doi.org/10.1089/cap.2019.0036
Abstract
Objectives
Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neuropsychiatric disorder with increasing global prevalence and high heritability commonly diagnosed in childhood. Current pharmaceutical treatment options provide a poor long-term risk: benefit ratio. Nutrition has significant effects on neurological functioning, and increasing evidence exists to support the use of multinutrients as alternative treatment for ADHD. The goal of this study is to assess the efficacy and tolerability of a multinutrient supplement as an alternative treatment for ADHD and co-occurring mood dysregulation symptoms.
Methods
The Multinutrients in ADHD Youth study is a fully-funded, multi-site, randomized double-blinded clinical trial for adolescents ages 6–12 years (n = 135). The study is 16 weeks in total, with an 8-week randomized controlled trial (RCT) followed by an 8-week open label (OL) phase. During the RCT phase, participants are assigned to either the treatment or placebo group at a 3:2 ratio. Study outcomes of ADHD symptoms include child's inattention, hyperactivity and mood dysregulation, which are assessed using validated questionnaires. Outcome data for the OL phase of the study were analyzed using end of RCT phase as baseline given that the RCT component of the study is still blinded.
Results
Preliminary findings based on the OL phase compared ADHD symptoms following 8 weeks of open label supplementation (n = 27 families). A significant decrease in symptom count was found for inattention (P ≤ 0.001), hyperactivity (P ≤ 0.001), ODD (P ≤ 0.001) and DMDD (P ≤ 0.001).
Conclusions
This study is the first adequately powered RCT in North America to investigate the effects of multinutrients supplements on ADHD symptoms among children. Preliminary findings indicate a trend in the improvements of ADHD symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity, ODD and DMDD in the OL phase of the study.
Funding Sources
Foundation for the Center of Excellence in Mental Health, Canada; The Ohio State University Department of Human Sciences, College of Education and Human Ecology; The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Clinical Research Center.

Multinutrients for ADHD Youth (MADDY) Trial: Preliminary Trends for Treatment
Madeline Stern, Leanna Perez, Jeanette Johnstone, Barbara Gracious, Brenda Leung, Eugene Arnold, Gabriella Tost, Irene Hatsu. Current Developments in Nutrition, Volume 3, Issue Supplement 1, June 2019, https://doi.org/10.1093/cdn/nzz050.P16-028-19
Abstract
Objectives: There is an increasing body of literature documenting the efficacy of micronutrients (vitamins and minerals) interventions for the treatment of psychiatric problems in the short term; however, long-term safety is largely unexplored. The goal of this observational study was to investigate the safety of two commercially available broad-spectrum micronutrient formulas (EMPowerplus† and Daily Essential Nutrients) given at doses above the Recommended Dietary Allowances for the long-term treatment of individuals with psychiatric symptoms.
Design: Participants on long-term treatment with micronutrients (medication-free) for psychiatric problems (attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder [ADHD, n = 21], anxiety/depression [n = 13]) were identified from ongoing research studies and the community through purchasing records. Seventeen children and 17 adults had blood tests to assess their full blood count, coagulation profile, liver and kidney function, fasting glucose, iron studies, key nutrients, and prolactin. Questionnaires assessed psychological/psychiatric functioning. Seventeen of the participants had completed the same measures pretreatment.
Results: The average length of consuming micronutrients was 2.66 years (standard deviation = 2.86). Excluding B12 (which was elevated for almost all participants), 94.6% of all blood test results were within the test reference ranges. One participant was diagnosed with hemochromatosis based on iron studies. No other clinically relevant adverse changes in blood results were identified pre- and post-treatment. No clinically significant adverse effects were reported. Post-treatment psychometrics identified that 85% of the participants were in nonclinical ranges for measures of ADHD, depression, anxiety, and stress.
Conclusions: We report preliminary evidence for the safety of long-term commercially available micronutrients, although questions remain. Overall, the substantial psychiatric benefits observed appear to outweigh the minimal observed risks in these participants. Screening for potential medical problems is recommended before initiating treatment. Long-term pharmacovigilance monitoring is required to ascertain any rare but significant adverse events.

An Observational Preliminary Study on the Safety of Long-Term Consumption of Micronutrients for the Treatment of Psychiatric Symptoms
Julia J. Rucklidge, PhD, Matthew J. F. Eggleston, MD, Breanne Ealam, BA (Hons), Ben Beaglehole, MD, and Roger T. Mulder, MD. J Altern Complement Med. 2019 Jun;25(6):613-622. doi: 10.1089/acm.2018.0352. Epub 2019 May 13.
Background: Intent-to-treat analyses from a randomized controlled trial showed significant between-group differences favouring micronutrient treatment on the Clinical Global Impression-Improvement, but no group differences on clinician, parent and teacher ratings of overall ADHD symptoms. There was an advantage of micronutrients over placebo in improving overall function, emotional regulation, aggression, and reducing impairment as well as improving inattention based on clinician but not parent observation. No group differences were observed on hyperactive-impulsive symptoms. We investigated predictors of response defined by pre-treatment variables.
Method: We conducted analyses of data from a clinical trial of children (7-12 years) with ADHD, whereby participants were randomized to receive micronutrients or placebo for 10 weeks followed by a 10 week open-label (OL) phase. We included only children who had been exposed to micronutrients for a full 10 week period and demonstrated satisfactory adherence, either in RCT phase (n = 40) or OL phase (those who received placebo during RCT phase; n = 31). Seven outcomes were examined: change in ADHD symptoms (clinician/parent), ADHD responder, overall responder, change in mood, change in functioning, and change in aggression. Demographic, developmental variables, current clinical and physical characteristics, MTHFR genotype at two common variants, and pre-treatment serum/plasma levels (vitamin D, B12, folate, zinc, copper, iron, ferritin, potassium, calcium, magnesium, and homocysteine) were all considered as putative predictors.
Results: Substantial nutrient deficiencies pre-treatment were observed only for vitamin D (13%) and copper (15%), otherwise most children entered the trial with nutrient levels falling within expected ranges. Regression analyses showed varying predictors across outcomes with no one predictor being consistently identified across different variables. Lower pre-treatment folate and B12 levels, being female, greater severity of symptoms and co-occurring disorders pre-treatment, more pregnancy complications and fewer birth problems were identified as possible predictors of greater improvement for some but not all outcome measures although predictive values were weak. Lower IQ and higher BMI predicted greater improvement in aggression.
Conclusions: This study replicates Rucklidge et al. (2014b) showing the limited value of using serum nutrient levels to predict treatment response although we cannot rule out that other non-assayed nutrient levels may be more valuable. Additionally, no specific demographic or clinical characteristics, including MTHFR genetic status, were identified that would preclude children with ADHD from trying this treatment approach.

Can we predict treatment response in children with ADHD to a vitamin-mineral supplement? An investigation into pre-treatment nutrient serum levels, MTHFR status, clinical correlates and demographic variables
Rucklidge JJ, Eggleston MJF, Darling KA, Stevens AJ, Kennedy MA, Frampton CM. Can we predict treatment response in children with ADHD to a vitamin-mineral supplement? An investigation into pre-treatment nutrient serum levels, MTHFR status, clinical correlates and demographic variables. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2019 Mar 8;89:181-192.
Exposure times and dosage required for dietary components to modify DNA methylation patterns are largely unknown.
Aim: This exploratory research represents the first genome-wide analysis of DNA methylation changes during a randomized-controlled-trial (RCT) for dietary supplementation with broad spectrum vitamins, minerals and amino acids in humans.
Methods: Genome-wide changes in methylation from paired, peripheral blood samples were assessed using the Infinium Methylation EPIC 850 K array.
Results: Methylation increased at 84% of the most significant differentially methylated CpGs; however, none showed significance after adjustment for genome-wide testing.
Conclusion: Micronutrient supplementation is unlikely to have a substantial biological effect on DNA methylation over 10 weeks; however, the trend toward hypermethylation that we observed is likely to become more marked with longer exposure periods.

Methylomic changes in response to micronutrient supplementation and MTHFR genotype.
Stevens AJ, Rucklidge JJ, Darling KA, Eggleston MJ, Pearson JF, Kennedy MA. Epigenomics. 2018 Sep 4;10(09):1201-14.
Background: Healthcare costs are skyrocketing, with mental health treatment amongst the most expensive, especially when hospitalization is involved. According to the Mental Health Commission of Canada, one in five Canadians is living with a mental disorder in any given year, at an annual cost of $50 billion. In light of this societal burden, alternative approaches are being evaluated, such as brief psychotherapy by phone, peer support, and, as part of the emerging field of nutritional mental health, treatment with micronutrients (minerals and vitamins). Effectiveness of micronutrients has been demonstrated for many types of psychiatric symptoms, in about 45 studies of formulas that are either multinutrient (e.g., several B vitamins) or broad-spectrum (usually over 20 minerals and vitamins). Although this literature demonstrates therapeutic benefits, the potential economic impact of micronutrient treatment has been evaluated in only one case study of childhood psychosis.
Methods: The current case study was initiated to evaluate mental health-related hospitalization costs from 1997 to 2003 for a female adult diagnosed with various mood and psychotic symptoms. She was treated for the first 5 years with conventional methods and then subsequently with a broad-spectrum micronutrient formula.†
Results: The patient’s annual mental health hospitalization costs during conventional treatment averaged $59,864 across 5 years (1997–2001), with a peak annual cost of about $140,000. Since transitioning to broad-spectrum micronutrients, she has incurred no provincial hospitalization costs for mental health care, though her self-funded costs are currently $720/year for the micronutrients.
Conclusion: Further exploration of the treatment of mental health problems with broad-spectrum micronutrient formulas has the potential to make two significant contributions: improved mental health, and decreased costs for governments.

Hospitalization cost of conventional psychiatric care compared to broad‑spectrum micronutrient treatment: literature review and case study of adult psychosis
Kaplan BJ, Isaranuwatchai W, Hoch JS. Int J Ment Health Syst. 2017 Jan 31;11:14.
BACKGROUND:
Evaluation of broad-spectrum micronutrient (vitamins and minerals) treatment for childhood ADHD has been limited to open-label studies that highlight beneficial effects across many aspects of psychological functioning.
METHOD:
This is the first fully blinded randomized controlled trial of medication-free children (n = 93) with ADHD (7-12 years) assigned to either micronutrients (n = 47) or placebo (n = 46) in a 1:1 ratio, for 10 weeks. All children received standardized ADHD assessments. Data were collected from clinicians, parents, participants and teachers across a range of measures assessing ADHD symptoms, general functioning and impairment, mood, aggression and emotional regulation.
RESULTS:
Intent-to-treat analyses showed significant between-group differences favouring micronutrient treatment on the Clinical Global Impression-Improvement (ES = 0.46), with 47% of those on micronutrients identified as 'much' to 'very much' improved versus 28% on placebo. No group differences were identified on clinician, parent and teacher ratings of overall ADHD symptoms (ES ranged 0.03-0.17). However, according to clinicians, 32% of those on micronutrients versus 9% of those on placebo showed a clinically meaningful improvement on inattentive (OR = 4.9; 95% CI: 1.5-16.3), but no group differences on improvement in hyperactive-impulsive symptoms (OR = 1.0; 95% CI: 0.4-2.5). Based on clinician, parent and teacher report, those on micronutrients showed greater improvements in emotional regulation, aggression and general functioning compared to placebo (ES ranged 0.35-0.66). There were two dropouts per group, no group differences in adverse events and no serious adverse events identified. Blinding was successful with guessing no better than chance.
CONCLUSIONS:
Micronutrients improved overall function, reduced impairment and improved inattention, emotional regulation and aggression, but not hyperactive/impulsive symptoms, in this sample of children with ADHD. Although direct benefit for core ADHD symptoms was modest, with mixed findings across raters, the low rate of adverse effects and the benefits reported across multiple areas of functioning indicate micronutrients may be a favourable option for some children, particularly those with both ADHD and emotional dysregulation. Trial registered with the Australian New Zealand Clinical Trials Registry ACTRN12613000896774.

Vitamin-mineral treatment improves aggression and emotional regulation in children with ADHD: a fully blinded, randomized, placebo-controlled trial.
Rucklidge JJ, Eggleston MJF, Johnstone JM, Darling K, Frampton CM. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2017 Oct 2.
Objective: Despite widespread use, there is little data investigating the long-term impact of micronutrients on psychiatric disorders. This study investigated the naturalistic outcome 1-year post-baseline of a randomized controlled trials (RCT) that compared micronutrients with placebo in 80 adults with ADHD.
Method: All participants were contacted and clinician-rated questionnaires completed.
Results: A total of 72 (90%) of the sample participated; although there was significant regression in psychiatric functioning from the end-of-trial on all measures, outcomes remained significantly improved from baseline. Dominant treatment from the end-of-treatment to follow-up was investigated as a mediator of outcome; those staying on the micronutrients performed better than those who switched to medications or discontinued micronutrients. Cost was the most substantial reason why people stopped micronutrient treatment. Conclusion: For the small number of participants who stayed on micronutrients, the benefits conferred through the controlled trial were maintained. The results are limited by small sample, lack of blinding, expectation, and reliance on self-report of symptoms.

Vitamin–Mineral Treatment of ADHD in Adults: A 1-Year Naturalistic Follow-Up of a Randomized Controlled Trial
Rucklidge JJ, Frampton CM, Gorman B, Boggis A. Vitamin-Mineral Treatment of ADHD in Adults. J Atten Disord. 2017 Apr;21(6):522-532.
Emotional dyscontrol following traumatic brain injury (TBI) impairs social relationships and employability. Micronutrients (minerals, vitamins) stabilize emotional lability in psychiatric patients, and various individual nutrients have been used to treat experimental brain injury in laboratory animals in the acute phase. However, the current case report appears to be the first documentation of micronutrients resulting in normalization of emotion regulation in a long-standing brain injury in a human.
Case presentation: A broad-spectrum formula of micronutrients† was evaluated in a 35-year-old male who had incurred a severe TBI eight years previously. Resolution of most post-TBI symptoms was achieved during those eight years, but not his episodic loss of emotional control, which psychiatrists evaluated as being permanent. The trial of micronutrients began after five weeks of baseline symptom monitoring with a mood stability scale. By three months mood stability had improved markedly according to data submitted by two raters (the patient and his clinician) who were blind to each other’s evaluations. Data collection continued for one year, showing significant improvement (p<.0001), at which time the patient reported that his emotional control had returned to his pre-TBI level. The improvements led to his establishing his own business and improving his family relationships.
Micronutrient treatment resulted in resolution of this patient’s longstanding post-TBI emotional dyscontrol. Broad-spectrum micronutrient formulas are showing benefit for the treatment of mood lability in various types of psychiatric patients; this report indicates there is also potential value in using them for the emotional dyscontrol found in post-TBI patients.

Micronutrient Treatment of Emotional Dyscontrol Following Traumatic Brain Injury
Kaplan, B. J., Leaney, C., Tsatsko, E. Annals of Psychiatry and Mental Health. 29 August 2016.
Insomnia is a debilitating condition causing psychological distress and frequently comorbid with other mental health conditions. This study examined the effect of 8 weeks of treatment by broad spectrum micronutrients (Hardy Nutritionals® Optimal Balance, formerly known as Daily Self Defense™) on insomnia using a multiple-baseline-across-participants open-label trial design. Seventeen adults were randomized to 1-, 2-, or 3-week baseline periods (14 completed). Self-report measures were the Consensus Sleep Diary–Morning (CSD-M), the Pittsburgh Insomnia Rating Scale (PIRS), and the Depression, Anxiety, Stress Scale (DASS). Baselines were generally stable. Treatment completers reported reliable and clinically significant change in insomnia severity (PIRS), in depression, stress, and anxiety (DASS), and on at least two aspects of sleep measured by the CDS-M. All completers were treatment-compliant, and side effects were minimal. Nutritional supplementation is shown to be a novel, beneficial treatment for insomnia in adults. Follow-up research using placebo-controlled designs as well as comparisons to cognitive-behavioral and other treatments is recommended.

Effect of Micronutrients on Insomnia in Adults: A Multiple-Baseline Study
Joanna Lothian, Neville M. Blampied, Julia J. Rucklidge. Clinical Psychological Science. May 23, 2016.doi:10.1177/2167702616631740
After devastating flooding in southern Alberta in June 2013, we attempted to replicate a New Zealand randomised trial that showed that micronutrient (minerals, vitamins) consumption after the earthquakes of 2010-11 resulted in improved mental health. Residents of southern Alberta were invited to participate in a study on the potential benefit of nutrient supplements following a natural disaster. Fifty-six adults aged 23-66 were randomised to receive a single nutrient (vitamin D, n=17), a few-nutrients formula (B-Complex, n=21), or a broad-spectrum mineral/vitamin formula† (BSMV, n=18). Self-reported changes in depression, anxiety and stress were monitored for six weeks. Although all groups showed substantial decreases on all measures, those consuming the B-Complex and the BSMV formulas showed significantly greater improvement in stress and anxiety compared with those consuming the single nutrient, with large effect sizes (Cohen's d range 0.76-1.08). There were no group differences between those consuming the B-Complex and BSMV. The use of nutrient formulas with multiple minerals and/or vitamins to minimise stress associated with natural disasters is now supported by three studies. Further research should be carried out to evaluate the potential population benefit that might accrue if such formulas were distributed as a post-disaster public health measure.

A randomised trial of nutrient supplements to minimise psychological stress after a natural disaster
Kaplan BJ, Rucklidge JJ, Romijn AR, Dolph M. Psychiatry Res. 2015 Aug 30;228(3):373-9.
In January 2014, The British Journal of Psychiatry published the results of a double-blind controlled trial which provided evidence of efficacy for micronutrients† (vitamins and minerals) in the treatment of ADHD symptoms in adults, with a reassuring safety profile.
As a follow-up to the adult trial, and pilot study for a RCT in childhood ADHD, the Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychopharmacology recently published the results of a study which treated 14 children with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) using micronutrients† instead of medication.
The study demonstrated the clinical benefit, feasibility, and safety of broad-spectrum micronutrients in the treatment of childhood ADHD.
In the recently published study, medication-free children were treated with a micronutrient formula† for eight weeks and then taken off it for four weeks—with the on-off cycle repeating itself over a six-month period.
Modified Brinley plots revealed a reduction in ADHD symptoms, improved mood, and improved overall functioning during intervention phases, and deterioration in ADHD symptoms, mood, and overall functioning during the withdrawal phases. Reliable change analyses, Cohen's d and percent superiority effect sizes, 95% confidence intervals and t tests confirmed clinically and statistically significant change between the intervention and withdrawal phases, with large effect sizes observed pre- to post-exposure of micronutrients (d = 1.2–2.2) on ADHD symptoms during intervention phases. Seventy-one percent of participants showed at least a 30% decrease in ADHD symptoms by the end of the second treatment phase, and 79% were identified as “much improved” or “very much improved” at the end of the second phase (5 months) based on the clinician-rated CGI when considering functioning generally. The SDQ showed that these benefits occurred across other areas of functioning including emotional symptoms, conduct problems, and prosocial behaviours. The children's self-reports confirmed the improvements. Excellent adherence to treatment occurred throughout, side effects were mild and transitory, and no safety issues were identified through blood analyses.
The researchers said the results were so effective that some parents were reluctant to take their children off the micronutrients† for the full four weeks. They noted “When they came off the micronutrients†, some children’s symptoms returned within days, which was a good indication of their effectiveness.”

Clinically Significant Symptom Reduction in Children with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder Treated with Micronutrients: An Open-Label Reversal Design Study
Gordon HA, Rucklidge JJ, Blampied NM, Johnstone JM. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol. 2015 Dec;25(10):783-98. doi: 10.1089/cap.2015.0105. PubMed PMID: 26682999; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC4702182.
A micronutrient formulation co-developed† by Hardy Nutritionals® founder David Hardy, showed “statistically robust improvements” in the first-ever double-blind study to test the effectiveness and safety of a multivitamin-mineral supplement in adults with ADHD. Researchers from the University of Canterbury and the University of Otago, New Zealand, randomized 80 adults diagnosed with ADHD to take either the micronutrient formulation or identical-looking placebo pills for 8 weeks. Most of the study participants had at least one psychiatric diagnosis in addition to ADHD. Additional diagnoses included multiple anxiety disorders, major depressive disorder, dysthymia, bipolar disorder, reading disability, and alcohol/substance misuse or dependence. The nutrient group reported more than double the improvement in attention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity symptoms, compared with the placebo group. Clinical psychologists rated more than twice as many people in the nutrient group ‘very much’ or ‘much’ improved in overall symptoms. They also rated moderate and severely depressed participants in the nutrient group as having nearly double the improvement in depression symptoms. Researchers found that the micronutrients were completely safe; there were no differences in side effects between the two groups.

Vitamin–mineral treatment of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder in adults: double-blind randomised placebo-controlled trial.
Rucklidge JJ, Frampton CMA, Gorman B, Boggis A. The British Journal of Psychiatry. 2014 Feb;204(2): doi: 10.1192/bjp.bp.113.132126 [Epub ahead of print]
Dr. Julia Rucklidge conducted nutrient assays on study participants in her 8 week double-blind RCT using micronutrient treatment† for adult ADHD. Using this extensive data set, she performed a post-hoc analysis of the original study in an attempt to determine if blood levels of nutrients in adult ADHD patients could be used to predict whether or not they would respond to micronutrient treatment. The blood markers measured were Vitamin D, Vitamin B12, Folate, Iron, Zinc, Copper, and Ferritin.
With the exception of Vitamin d (27% of participants deficient), nutrient deficiencies were slight or non-existent for the majority of participants at the beginning of the trial. In spite of the fact that only one participant exhibited iron deficiency, low iron levels were associated with higher baseline depression scores (p=0.009). No other nutrient significantly correlated with baseline psychiatric scores.
Throughout the course of the trial, micronutrient treatment was associated with significant increases in blood Vitamin D, Vitamin B12, and Folate (all p<0.001), but only Vitamin D was also identified as one of the nutrient markers that showed a statistically significant effect on treatment response.
The nutrient markers affecting treatment response were: ferritin, vitamin D, and copper. Greater ferritin at baseline correlated with being an ADHD responder (p=0.027). (ADHD response was defined as ≥30% decrease in symptom scores for a comprehensive combination of outcome measures. Of the 64 original study participants with complete nutrient assays, 39 (60.9%) were identified as ADHD responders.) Lower baseline vitamin D was predictive of greater improvements in depression (p=0.011) and global functioning (p=0.045) scores, and lower baseline copper levels predicted greater response in the depression (p=0.002) and clinical global improvement (p=0.007) outcome measures.
From among the non-nutrient variables measured, the researchers identified developmental history as the only noticeable predictor of response. This means that people with a history of developmental risk factors (e.g., slow to talk, walk, read, toilet train) may benefit even more from micronutrient treatment than those who developed normally as a child. It is also worth noting that several participants who reported alcohol or drug use at baseline later reported a reduction or cessation of these behaviours during micronutrient treatment, suggesting the possible value of nutrients in addiction therapy.
Only a few significant associations were identified between baseline biomarkers and outcomes, but, despite the difficulty in predicting the outcome for any given person, micronutrient treatment proved very effective – providing substantial ADHD symptom reduction for over half of the adults in this study.

Moderators of treatment response in adults with ADHD treated with a vitamin-mineral supplement
Rucklidge JJ, Johnstone J, Gorman B, Boggis A, Frampton CM. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2014 Apr 3;50:163-71. doi:10.1016/j.pnpbp.2013.12.014. Epub 2013 Dec 26. PubMed PMID: 24374068.
Following the devastating New Zealand earthquake of February 22, 2011, Dr. Rucklidge et al. conducted a 4 week randomized trial in which anxiety and stress were significantly reduced in adults given various doses of micronutrients† when compared to untreated individuals. One year later Dr. Rucklidge followed up with the study participants to evaluate long-term outcomes.
Of the original 91 participants who took micronutrients in the original trial, 64 (70.3%) completed the follow-up questionnaires, as did 21 (72.4%) of the original control group. Both groups improved over their post-earthquake baseline scores, and the risk of PTSD declined drastically for both groups. However, the nutrient-treated group reported significantly lower stress and greater improvements in mood and energy than the control group one year later, even after adjusting for baseline differences (p<0.001).
Those who stayed on micronutrients through to follow-up or who stopped all treatment reported better psychological functioning than those who switched to other treatments, including medications (p<0.023). The researchers concluded that, while disaster survivors improve psychologically over time regardless of whether or not they receive an intervention, taking micronutrients during the acute phase immediately following a disaster might result in significantly better short and long-term outcomes.

Psychological functioning 1 year after a brief intervention using micronutrients to treat stress and anxiety related to the 2011 Christchurch earthquakes: a naturalistic follow-up
Rucklidge JJ, Blampied N, Gorman B, Gordon HA, Sole E. Hum Psychopharmacol. 2014 May;29(3):230-43. doi: 10.1002/hup.2392. Epub 2014 Feb 19. PubMed PMID: 24554519.
Researchers collected safety, tolerability, and serum micronutrient concentration data and their correlations with mood changes from an 8-week pilot feasibility study of a broad spectrum micronutrient formula.†
Adverse effects were mild and transient, and chiefly initial insomnia or GI upset. No differences occurred in BMI (p = 0.310) or waist-hip ratio (WHR; p = 0.674) pre- to post-supplementation.
In this open prospective study, short-term use of the micronutrient formula in children with BPSD appeared safe and well-tolerated, with a side effect profile preferable to first-line psychotropic drugs for pediatric bipolar spectrum disorders. A double-blind, randomized clinical trial is feasible, appears safe, and is warranted by open-label clinical outcomes and plausible mechanisms of action combined with documentation of increased serum concentrations of specific micronutrients.

Nutritional and Safety Outcomes from an Open-Label Micronutrient Intervention for Pediatric Bipolar Spectrum Disorders
Frazier EA, Gracious B, Arnold LE, Failla M, Chitchumroonchokchai C, Habash D, Fristad MA. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol. 2013 Oct;23(8):558-67. doi: 10.1089/cap.2012.0098.
A 24-year-old woman who experienced dramatic improvement in her ADHD and depression symptoms for more than 2 years while taking a micronutrient formulation co-developed† by Hardy Nutritionals® founder David Hardy later experienced a recurrence of her former psychiatric symptoms as a result of a severe yeast infection. Her physical symptoms included an overall flu-like feeling; a chronic sore throat and runny nose; cravings for sugary and starchy foods; gastrointestinal cramps; and rashes and itching on her legs, groin, genital and rectal areas. Psychiatric symptoms included severe moodiness, inability to experience pleasure, and chronic irritability. These physical and psychiatric symptoms persisted for several months despite her ongoing use of a prescription antifungal cream. The woman began taking four capsules of olive leaf extract (identical to our Hardy Nutritionals™ Olive Leaf Extract) as well as two capsules of probiotics (identical to our Hardy Nutritionals™ Greens & Probiotics) daily to treat the yeast infection, in addition to her regular therapeutic dose of the micronutrients. After a week and a half, the woman’s physical and psychiatric symptoms both improved, including disappearance of her rashes, cessation of the chronic itching, elimination of her runny nose, and improved mood and energy levels. After 2 months, she had returned to her previous level of function. During a year of follow-up, researchers found that the woman continued to enjoy relief from the physical and psychiatric symptoms caused by the yeast infection as long as she continued to take the Olive Leaf Extract.

Could yeast infections impair recovery from mental illness? A case study using micronutrients and olive leaf extract for the treatment of ADHD and depression.
Rucklidge JJ. Advances in Mind-Body Medicine. 2013 Summer;27(3):14-8.
Scientists observed while conducting previous studies that many study participants whose psychiatric symptoms were treated successfully with a micronutrient formulation co-developed† by Hardy Nutritionals® founder David Hardy tended to reduce or eliminate use of alcohol, cigarettes and cannabis on their own. This study details one case in which on-off micronutrient use resulted in off-on cigarette and cannabis smoking as well as off-on psychiatric symptoms. Micronutrients provide the necessary precursors and cofactors for adequate neurotransmitter production and regulation. In this way, micronutrients assist with mood regulation, help reduce anxiety, and directly affect brain reward circuitry, all of which can help individuals to successfully stop drug use.

Use of micronutrients attenuates cannabis and nicotine abuse as evidenced from a reversal design: a case study.
Harrison R, Rucklidge JJ, Blampied N. Journal of Psychoactive Drugs. 2013 Jun;45(2):168-178.
An 11-year-old boy with a 3-year history of mental illness and psychiatric medication treatment was transitioned to a micronutrient formulation co-developed† by Hardy Nutritionals® founder David Hardy. The boy was diagnosed with multiple psychiatric disorders, including obsessive-compulsive disorder, generalized anxiety disorder, social anxiety disorder, and psychosis—not otherwise specified. The boy’s anxiety, obsessive-compulsive, and psychotic symptoms decreased significantly when he took the vitamin-mineral formulation, and his progress was maintained through a 4-year follow-up. A cost comparison revealed that the boy’s micronutrient treatment cost less than 1% of his former inpatient mental health care.
Efficacy and cost of micronutrient treatment of childhood psychosis.
Rodway M, Vance A, Watters A, Lee H, Bos E, Kaplan BJ. BMJ Case Reports. 2012 Nov 9;2012.
Following a 6.3-magnitude earthquake in Christchurch, New Zealand, researchers randomized 91 earthquake survivors to take one of two vitamin-mineral formulas (Berocca Performance or a micronutrient formulation co-developed† by Hardy Nutritionals® founder David Hardy. Then they measured symptoms of situation-induced depression, anxiety, and stress in these individuals, as well as 25 additional people who took no supplement (a control group). After 4 weeks, 20% of the control group, 43% of the Berocca Performance group, and 74% of the group taking the micronutrients showed significant improvement in depression, anxiety, and stress symptoms. Researchers concluded that this study supports micronutrients as an inexpensive and practical treatment for acute stress following a natural disaster, with a slight advantage to higher doses.

Shaken but unstirred? Effects of micronutrients on stress and trauma after an earthquake: RCT evidence comparing formulas and doses.
Rucklidge JJ, Andridge R, Gorman B, Blampied N, Gordon H, Boggis A. Human Psychopharmacology. 2012 Sep;27(5):440-54.
Researchers investigated the therapeutic effects of a micronutrient formulation co-developed† by Hardy Nutritionals® founder David Hardy in 7 children with bipolar disorder. The children’s additional psychiatric diagnoses included attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, oppositional defiant disorder, major depressive disorder, generalized anxiety disorder, conduct disorder, and obsessive-compulsive disorder. The children experienced a 37% decrease in depression scores and a 45% decrease in mania scores over 8 weeks. Side effects were minor and transient—mostly temporary gastric discomfort.

Feasibility of a nutritional supplement as treatment for pediatric bipolar spectrum disorders.
Frazier EA, Fristad MA, Arnold LE. Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine. 2012 Jul;18(7):678-85.
Scientists compiled safety data from all published and unpublished studies that used a micronutrient formulation co-developed† by Hardy Nutritionals® founder David Hardy which has been widely researched in the mental health field. Biological safety data from six sources, including 144 children and adults, showed no occurrences of clinically meaningful negative outcomes/effects or abnormal blood tests that could be attributed to toxicity. Adverse event information from six studies involving 157 children and adults included reports of minor, transitory headache and nausea. Only one of the studies permitted a direct comparison between tolerability of the micronutrient treatment and medications: children and adults treated with micronutrients showed significantly fewer adverse events and significantly less weight gain compared with those taking medications.

Systematic review of safety and tolerability of a complex micronutrient formula used in mental health.
Simpson JS, Crawford SG, Goldstein ET, Field C, Burgess E, Kaplan BJ. BioMed Central Psychiatry. 2011 Apr 18;11:62.
Researchers studied the impact of a micronutrient formulation co-developed† by Hardy Nutritionals® founder David Hardy on neurocognitive functioning in 14 adults with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and severe mood dysregulation over an 8-week period. Significant improvement was observed in the ADHD-micronutrient group, but not the control group, across a range of verbal abilities, including verbal learning, verbal cognitive flexibility and fluency, and verbal inhibition. These neurocognitive improvements were large and consistent with improved psychiatric functioning.

Can micronutrients improve neurocognitive functioning in adults with ADHD and severe mood dysregulation? A pilot study.
Rucklidge JJ, Harrison R, Johnstone J. Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine. 2011 Dec;17(12):1125-31.
A 7.1-magnitude earthquake in Christchurch, New Zealand created a natural experiment for measuring the protective effects of a micronutrient formulation co-developed† by Hardy Nutritionals® founder David Hardy on mood, anxiety and stress. Prior to the earthquake, researchers had assessed mood, anxiety and stress levels in a group of 33 adults diagnosed with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, and they chose to repeat the same measures after the earthquake. Scores showed that the 16 participants taking micronutrients were more resilient to the effects of the earthquake than the 17 individuals not taking any supplement. This effect was particularly marked for depression scores.

Post-earthquake psychological functioning in adults with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: positive effects of micronutrients on resilience.
Rucklidge JJ, Blampied, NM. New Zealand Journal of Psychology. 2011;40(4):51.
The role of good nutrition for resilience in the face of stress is a topic of interest, but difficult to study. A 7.1 earthquake took place in the midst of research on a micronutrient treatment† for Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), providing a unique opportunity to examine whether individuals with ADHD taking micronutrients demonstrated more emotional resilience post-earthquake than individuals with ADHD not taking micronutrients. Thirty-three adults with ADHD were assessed twice following the earthquake using a measure of depression, anxiety and stress also completed at some point pre-earthquake (baseline). Seventeen were not taking micronutrients at the time of the earthquake (control group), 16 were (micronutrient group). While there were no between-group differences one week post-quake (Time 1), at two weeks post-quake (Time 2), the micronutrient group reported significantly less anxiety and stress than the controls (effect size 0.69). These between group differences could not be explained by other variables, such as pre-earthquake measures of emotions, demographics, psychiatric status, and personal loss or damage following the earthquake. The results suggest micronutrients may increase resilience to ongoing stress and anxiety associated with a highly stressful event in individuals with ADHD and are consistent with controlled studies showing benefit of micronutrients for mental health.

Micronutrients reduce stress and anxiety following a 7.1 earthquake in adults with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder
Rucklidge JJ, Johnstone J, Harrison R, Boggis A. 2011. Psychiatry Research, 189:281-87.
Researchers documented the impact of a micronutrient formulation co-developed† by Hardy Nutritionals® founder David Hardy
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the effect of a 36-ingredient micronutrient formula consisting mainly of minerals and vitamins in the treatment of adults with both ADHD and severe mood dysregulation (SMD).
Method: 14 medication-free adults (9 men, 5 women; 18-55 years) with ADHD and SMD completed an 8-week open-label trial.
Results: A minority reported transitory mild side effects. Significant improvements were noted across informants (self, observer, clinician) on measures of inattention and hyperactivity/impulsivity, mood, quality of life, anxiety, and stress all with medium to very large effect sizes (all ps < .01); however, the mean of inattention remained in a clinical range whereas the means on measures of mood and hyperactivity/impulsivity were normalized. Follow-up data showed maintenance of changes or further improvement for those who stayed on the micronutrients.
Conclusions: Although this study, as an open trial, does not in itself prove efficacy, it provides preliminary evidence supporting the need for a randomized clinical trial of micronutrients as treatment for the more complex presentations of ADHD.

Effect of micronutrients on behaviour and mood in adults with ADHD: Evidence from an 8-week open label trial with natural extension.
Rucklidge JJ, Taylor MR, Whitehead KA. J Atten Disord. 2011 Jan;15(1):79-91.
Scientists analyzed data from 120 children with pediatric bipolar disorder who were treated with a micronutrient formulation co-developed† by Hardy Nutritionals® founder David Hardy for at least 6 months. 24% of these children also had a diagnosis of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Their results were compared with an additional 41 children who were diagnosed with ADHD alone. Children with a bipolar diagnosis showed a 59% decline in symptoms, whereas children with ADHD showed a 40% decrease in symptoms. The duration of symptom reduction suggests that benefits of micronutrient treatment were not attributable to placebo or expectancy effects. Of those taking psychiatric medications, more than half were able to completely discontinue them over a 6-month period. Medication use by the remainder of children was reduced by 74% during the same time period.

Database analysis of children and adolescents with bipolar disorder consuming a micronutrient formula.
Rucklidge JJ, Gately D, Kaplan BJ. BioMed Central Psychiatry. 2010 Sep 28;10:74.
Researchers documented the effects of a micronutrient formulation co-developed† by Hardy Nutritionals® founder David Hardy on psychiatric and neurocognitive functioning in a naturalistic off-on-off-on design. A 21-year old female with bipolar II disorder, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), social anxiety, and panic disorder began taking a vitamin-mineral formulation following a documented 8-year history of ongoing psychiatric symptoms that were not well managed by medications. After 8 weeks on the formula, she showed significant improvements in mood, anxiety, and hyperactivity/impulsivity. She then chose to come off the formula. After 8 weeks, her depression scores returned to pre-treatment levels, and anxiety and ADHD symptoms worsened dramatically. When the formula was reintroduced, all psychiatric symptoms showed gradual improvements. After one year, she was in remission of all mental illness diagnoses. Her neurocognitive changes mirrored behavioral changes, showing improved processing speed, variability in response, and verbal memory.

Successful treatment of bipolar disorder II and ADHD with a micronutrient formula: a case study.
Rucklidge JJ, Harrison R. CNS Spectrums. 2010 May;15(5):289-95.
Researchers compared psychiatric medication and micronutrient treatment approaches in 88 children with autism spectrum disorder. The micronutrient group (taking predominately a micronutrient formulation co-developed† by Hardy Nutritionals® founder David Hardy) improved significantly more than the medication group in key ways, including notably reduced irritability, anger, and intensity of self-injurious behaviors. The micronutrient-treated group also had dramatically lower treatment side-effects.

Micronutrients versus standard medication management in autism: a naturalistic case-control study.
Mehl-Madrona L, Leung B, Kennedy C, Paul S, Kaplan BJ. Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychopharmacology. 2010 Apr;20(2):95-103.
Researchers at the world-renowned Canadian Centre for Behavioural Neuroscience conducted a series of controlled studies with rats fed a micronutrient formulation co-developed† by Hardy Nutritionals® founder David Hardy to test its effects on brain injuries and brain-related disorders. Neuroscientists performed surgery on a group of young rats, removing either the entire frontal lobe of the brain or part of the parietal lobe. The researchers then fed one group of these rats Purina Rat Chow (considered to be an ideally fortified lab rat diet with 22 added vitamins and minerals) and another group the same base diet fortified with the more complete, specially-processed micronutrient formulation. Brain recovery was significantly enhanced in the micronutrient-fed rats. As the rats recovered, researchers observed that the micronutrient-fed rats showed significantly calmer behavior and dramatically improved cognitive function compared with Purina-fed rats. The brain cells of micronutrient rats were also more complexly-branched and better connected with neighboring cells than the brain cells of Purina-fed rats. The calmer behavior and enhanced cognitive function of micronutrient-treated rats are consistent with results documented by researchers around the world in many people with mood, anxiety, and behavioral disorders. The enhanced brain cell connectivity observed by researchers supports the use of micronutrient formulations for human brain recovery in conjunction with brain rehabilitation therapies.
Factors influencing frontal cortex development and recovery from early frontal injury.
Halliwell C, Comeau W, Gibb R, Frost DO, Kolb B. Developmental Neurorehabilitation. 2009;12(5):269-78.
Scientists analyzed data from 358 adults with a diagnosis of bipolar disorder who took a micronutrient formulation co-developed† by Hardy Nutritionals® founder David Hardy for 6 months or more. The adults’ overall symptom severity was 41% lower than baseline after 3 months, and 45% lower after 6 months. In addition, at 6 months, 53% of adults experienced greater than 50% improvement in symptoms, with 32% of adults experiencing greater than 75% improvement in symptoms. Symptom improvements at 6 months suggested that benefits of micronutrient treatment were not attributable to placebo or expectancy effects. Of those taking psychiatric medications, nearly half were able to discontinue them over a 6-month period. The remainder reduced their medication usage by 54% during the same time period. Adults who gradually eliminated their medications and took full recommended levels of the vitamin-mineral formulation experienced the greatest improvements in symptoms.

Database analysis of adults with bipolar disorder consuming a micronutrient formula.
Gately D, Kaplan BJ. Clinical Medicine Insights: Psychiatry. 2009 Apr;4:3-16.
Researchers detail an off-on-off-on trial of an 18-year-old male diagnosed with obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) and Asperger’s disordera who took a micronutrient formulation co-developed† by Hardy Nutritionals® founder David Hardy. The young man first underwent cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) for one year with a modest response. Within a year thereafter, his anxiety became severe again and he began to experience major depression. After 8 weeks of using a vitamin-mineral formulation, his mood stabilized, his anxiety reduced, and his obsessions were in remission. Treatment was then discontinued for 8 weeks, during which time his obsessions, anxiety, and mood worsened. Reintroduction of the micronutrient formula again improved mood, obsession and anxiety symptoms within 8 weeks. After taking the formulation for 6 months longer, he experienced further improvements in mood and anxiety symptoms.

Successful treatment of OCD with a micronutrient formula following partial response to Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): a case study.
Rucklidge JJ. Journal of Anxiety Disorders. 2009 Aug;23(6):836-40.
Researchers describe a 12-year-old boy who was diagnosed at age 6 with bipolar disorder. His diagnosis evolved to include psychotic features, generalized anxiety disorder and obsessive-compulsive disorder. Although he was treated with psychiatric medications for 6 years, he continued to experience many debilitating mood, anxiety, and obsessive-compulsive symptoms. During treatment with a micronutrient formulation co-developed† by Hardy Nutritionals® founder David Hardy, the boy’s global functioning notably improved. He began interacting more appropriately with peers, remained calm and playful throughout most of the day, slept throughout the night, remained focused and efficient while completing schoolwork, and experienced decreased compulsions. Eventually, his hallucinations also ceased and all diagnoses fully remitted. His symptoms remained stable during a 14-month follow-up period.

Multinutrient supplement as treatment: literature review and case report of a 12-year-old boy with bipolar disorder.
Frazier EA, Fristad MA, Arnold LE. Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychopharmacology. 2009 Aug;19(4):453-60.
Researchers treated nine unselected children with mood and behavioral problems with a micronutrient formulation co-developed† by Hardy Nutritionals® founder David Hardy. The children’s psychiatric diagnoses included attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, bipolar disorder, depression, oppositional defiant disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder, generalized anxiety disorder, Asperger syndrome, and Prader-Willi syndrome. After a minimum of 8 weeks of micronutrient treatment, the children’s behavior improved significantly in the following areas: anxious and depressed mood, thought problems, interpersonal relationship problems, attention problems, social problems, withdrawn behavior, disruptive behavior, delinquent behavior, aggressive behavior, and self-harm behavior.

Improved mood and behavior during treatment with a mineral-vitamin supplement: an open-label case series of children.
Kaplan BJ, Fisher JE, Crawford SG, Field CJ, Kolb B. Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychopharmacology. 2004 Spring;14(1):115-22.
Researchers describe two medication-free boys with unstable mood and explosive rage who took a micronutrient formulation co-developed† by Hardy Nutritionals® founder David Hardy followed by reversal and re-treatment. The boys’ diagnoses included pervasive developmental disorder with Asperger characteristics, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder, and autism. Both boys benefited significantly from the micronutrient formula: mood, angry outbursts, delinquent behavior, social and attention problems, and anxious/obsessional symptoms improved when initially treated, returned when they discontinued treatment, and remitted when the micronutrient treatment was reintroduced. During a follow-up of over 2 years, both boys continued to be stable while taking the micronutrient treatment.

Treatment of mood lability and explosive rage with minerals and vitamins: two case studies in children.
Kaplan BJ, Crawford SG, Gardner B, Farrelly G. Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychopharmacology. 2002 Fall;12(3):205-19.
Dr. Miles Simmons, a psychiatrist in private practice, followed nineteen patients diagnosed with bipolar I or bipolar II disorder for an average of 13 months while they took a micronutrient formulation co-developed† by Hardy Nutritionals® founder David Hardy. Sixteen of the 19 patients (84%) showed significant clinical improvement. Thirteen of 16 medicated patients were able to completely discontinue psychiatric medications over 3 to 10 weeks and maintain stability over an average follow-up period of 13 months.

Nutritional approach to bipolar disorder.
Simmons M. The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry. 2003 Mar;64(3):338; author reply 338-9.
After observing a 10-year-old boy's dramatic response to a micronutrient formulation co-developed† by Hardy Nutritionals® founder David Hardy, Dr. Charles Popper, a psychiatrist and psycho-pharmacologist at Harvard Medical School, treated 22 additional bipolar disorder-diagnosed patients in his private practice (10 adults, 9 adolescents, and 3 preadolescents) with the micronutrients. Nineteen of the 22 patients (86%) showed a positive response to micronutrient treatment. Of the 15 patients being treated with medications when they began the nutritional supplement, 11 patients remained stable during a follow-up period of 6 to 9 months without psychiatric medications.

Do vitamins or minerals (apart from lithium) have mood-stabilizing effects?
Popper CW. The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry. 2001 Dec;62(12):933-5.
Researchers treated 11 adults diagnosed with various types of bipolar disorder for an average of 44 weeks with a micronutrient formulation co-developed† by Hardy Nutritionals® founder David Hardy. The adults’ additional diagnoses included attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, dysthymic disorder, and obsessive-compulsive disorder. The adults experienced a 55% reduction in depression symptoms, a 60% reduction in mania symptoms, and a 66% reduction in general psychiatric symptoms. Their psychiatric medication use decreased by more than 50%. The only reported side effect, nausea, was infrequent, minor, and transitory.

Effective mood stabilization with a chelated mineral supplement: an open-label trial in bipolar disorder.
Kaplan BJ, Simpson JS, Ferre RC, Gorman CP, McMullen DM, Crawford SG. The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry. 2001 Dec;62(12):936-44.
